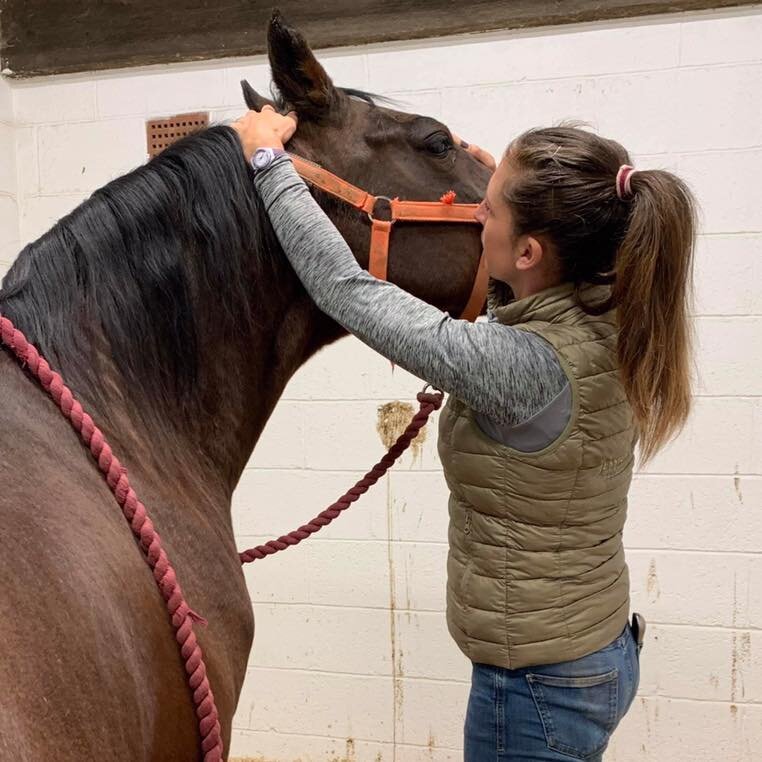
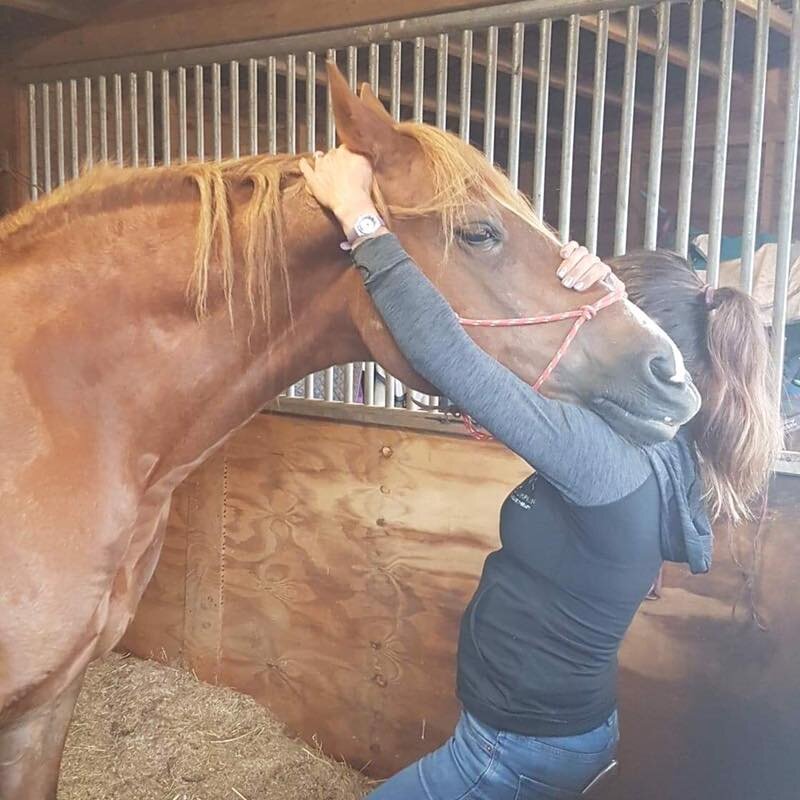
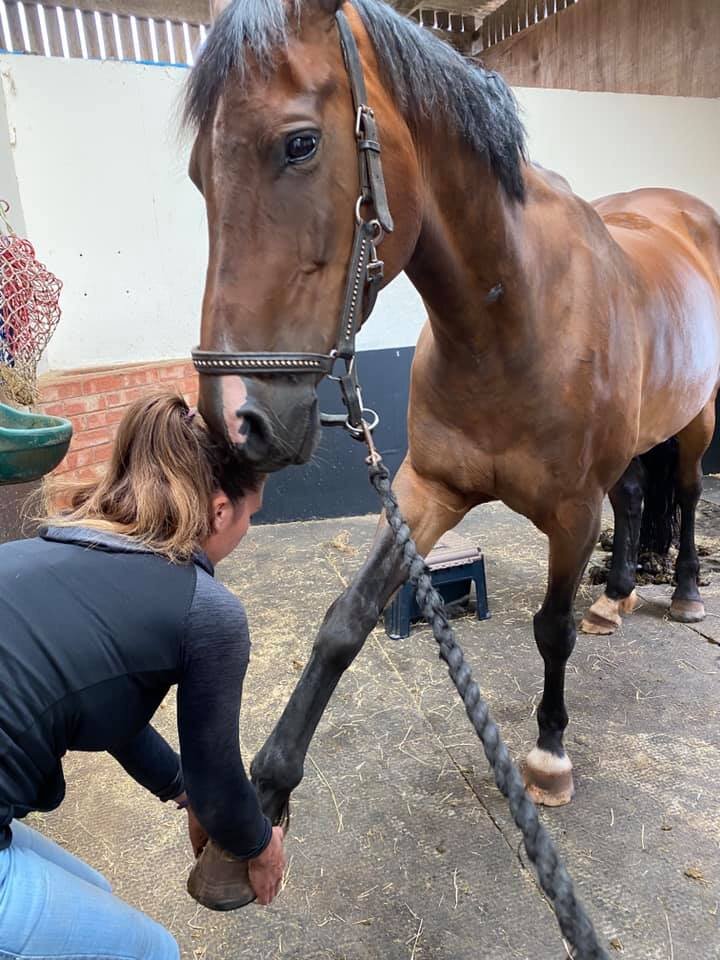
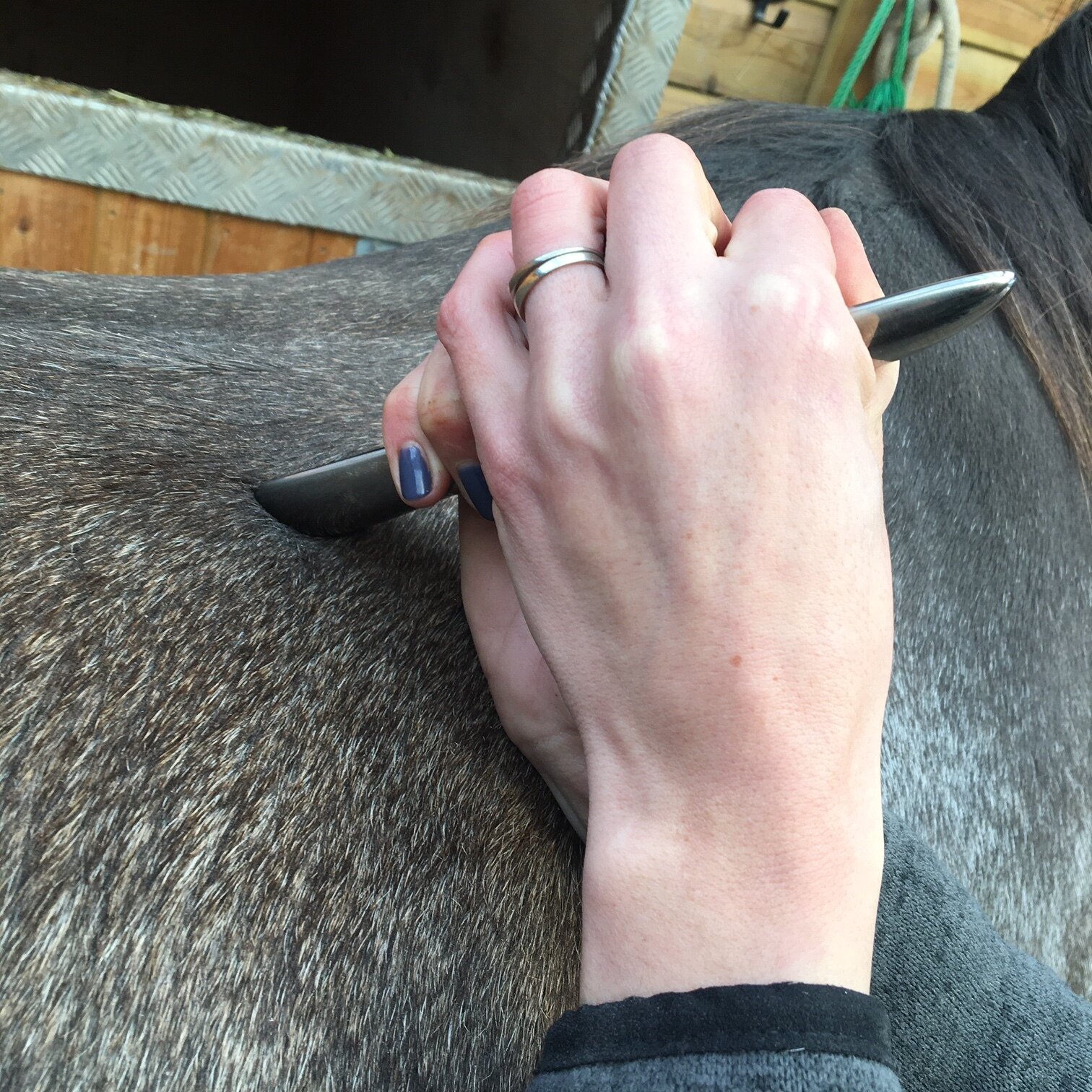
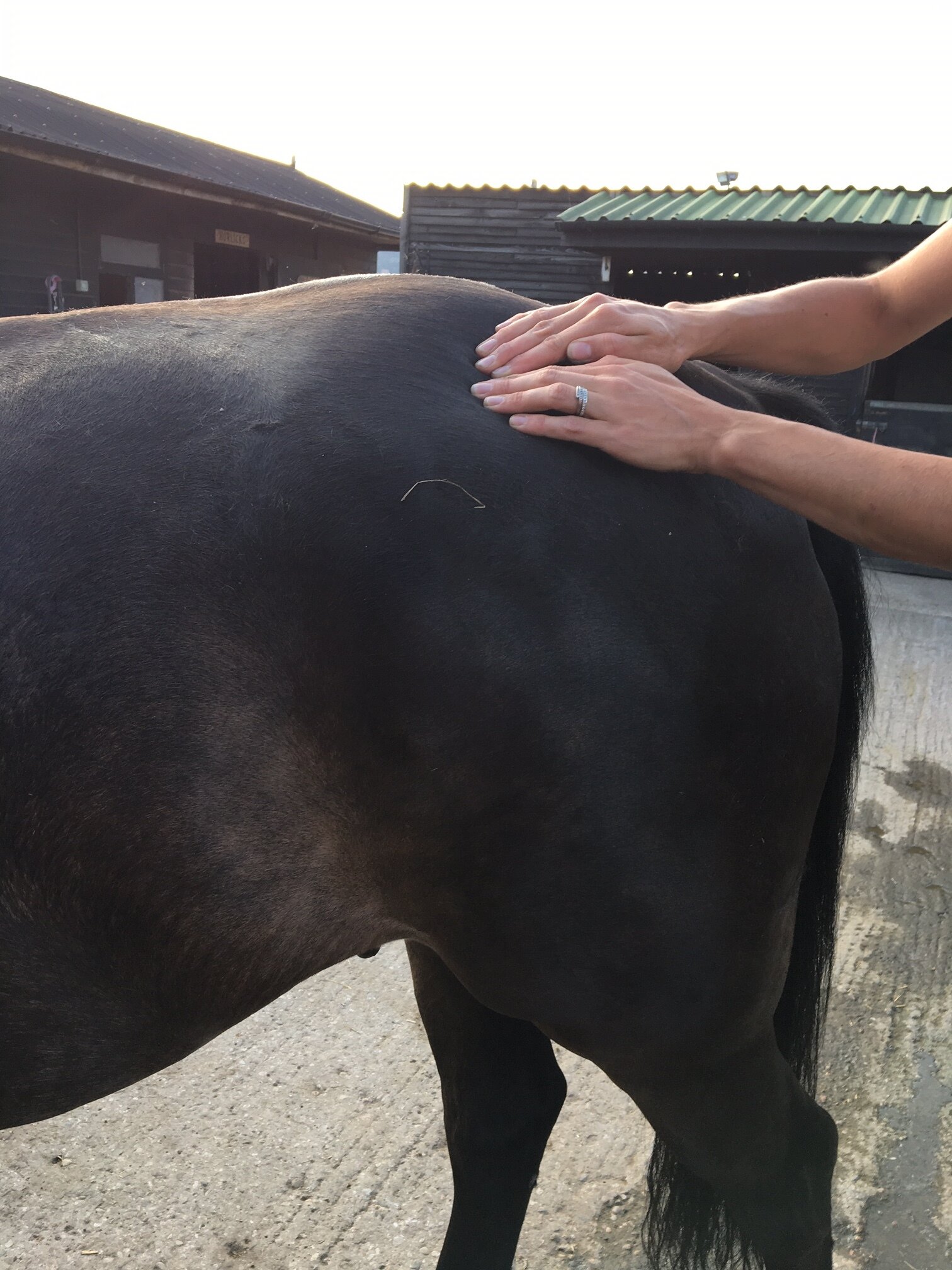
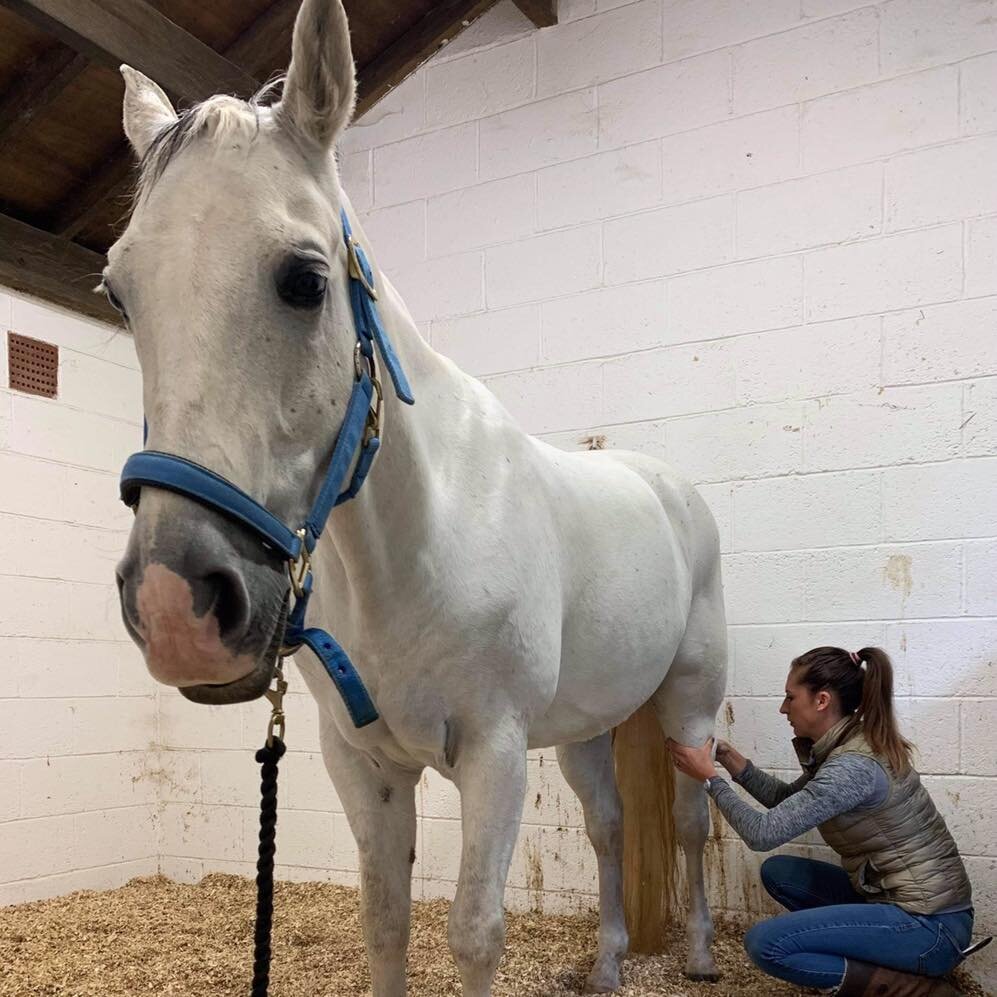
Introduction to Mobilisations
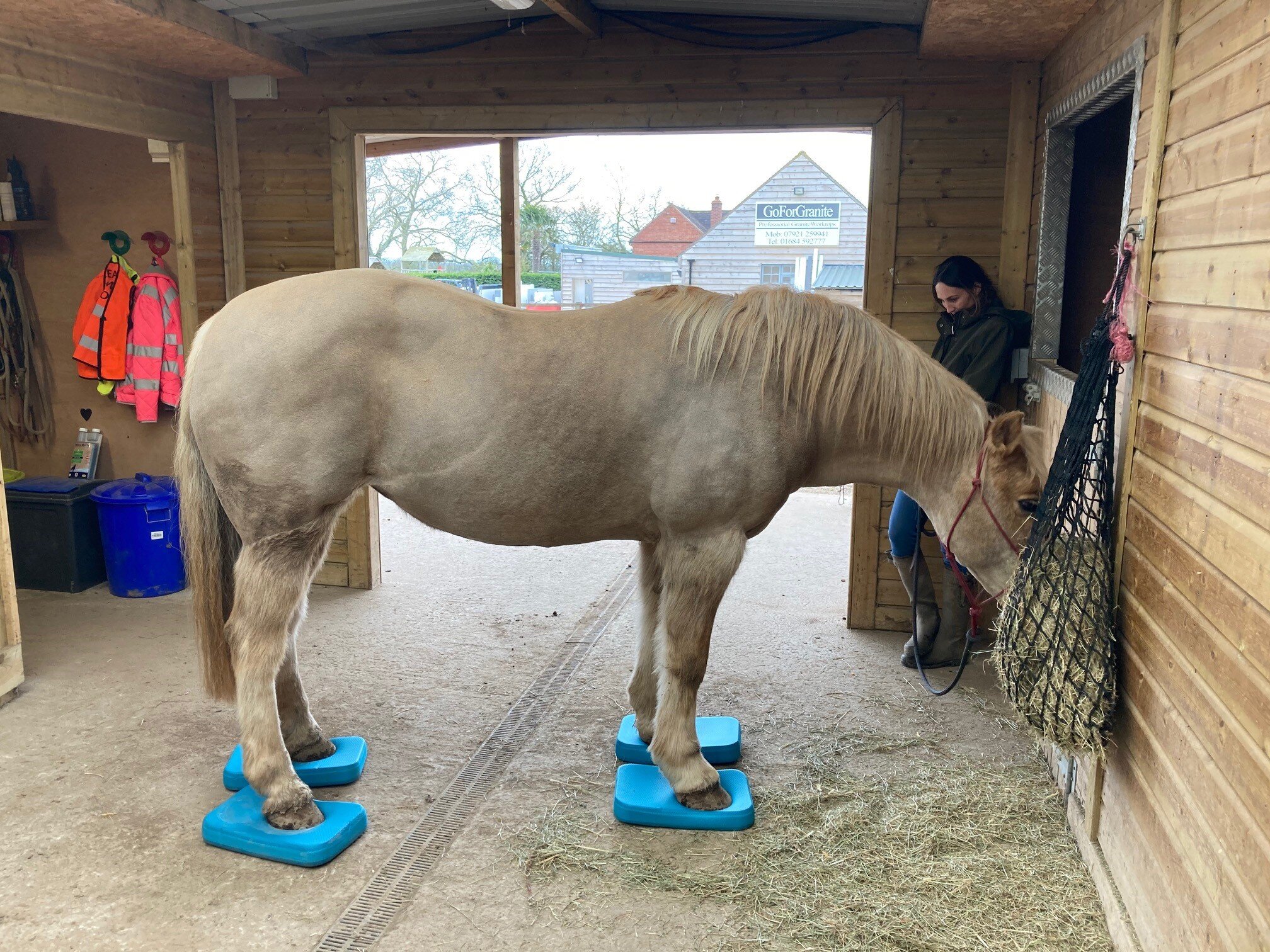
Joint mobilisation is characterised as non impulsive, repetitive joint movements induced within the passive range of joint motion with the purpose of restoring normal and symmetric joint range of motion, to stretch connective tissues, and to restore normal joint end feel.
Joint mobilisations are used to assess the quality and quantity of joint range of motion as well as a means of treating musculoskeletal disorders.
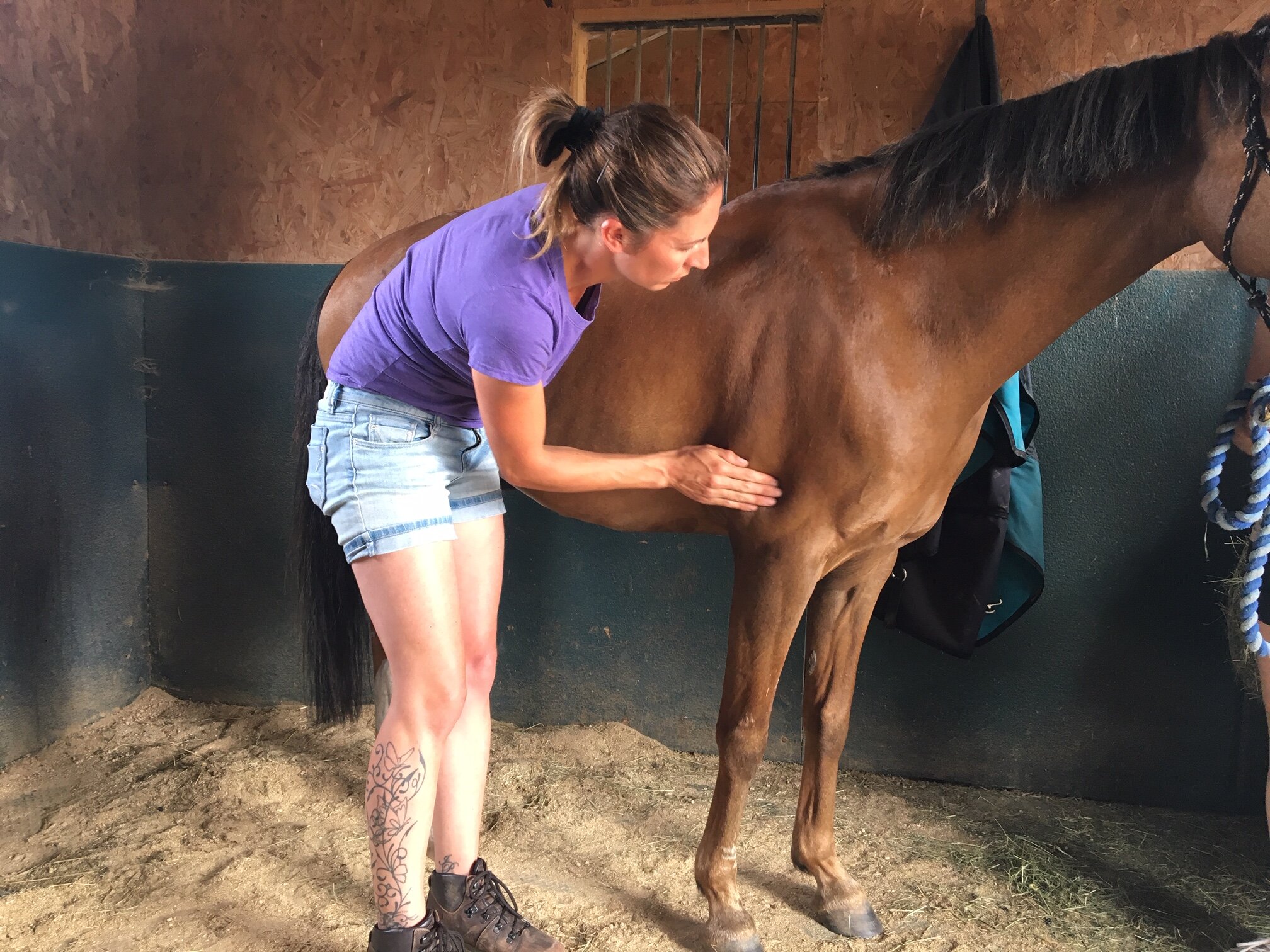
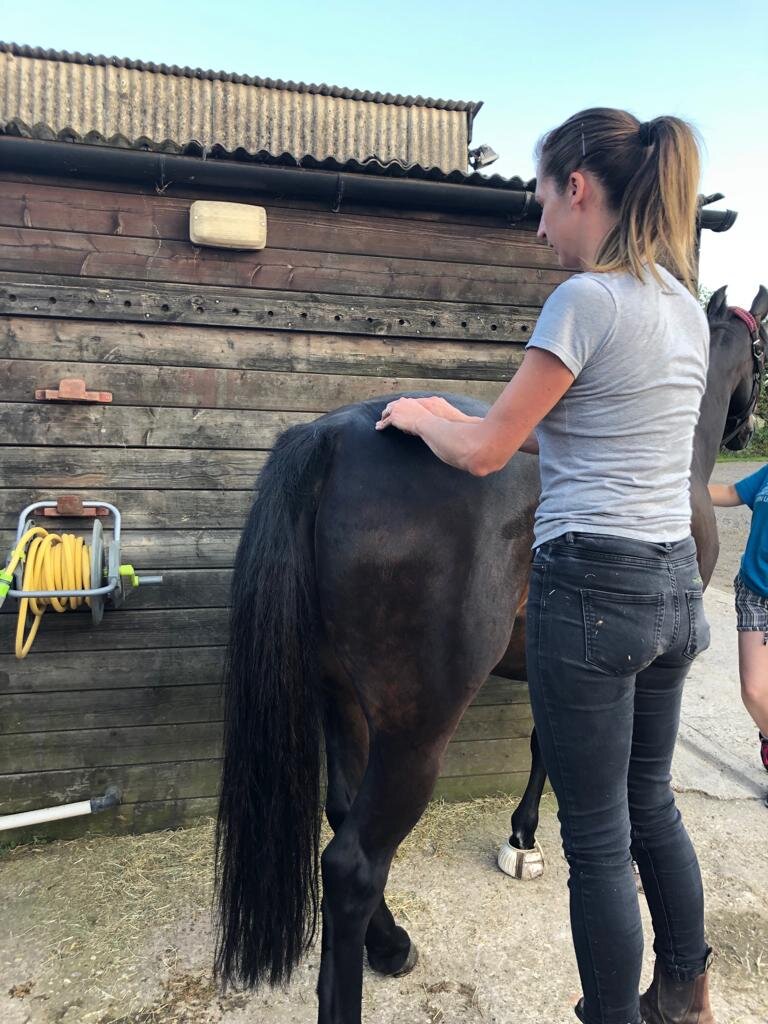
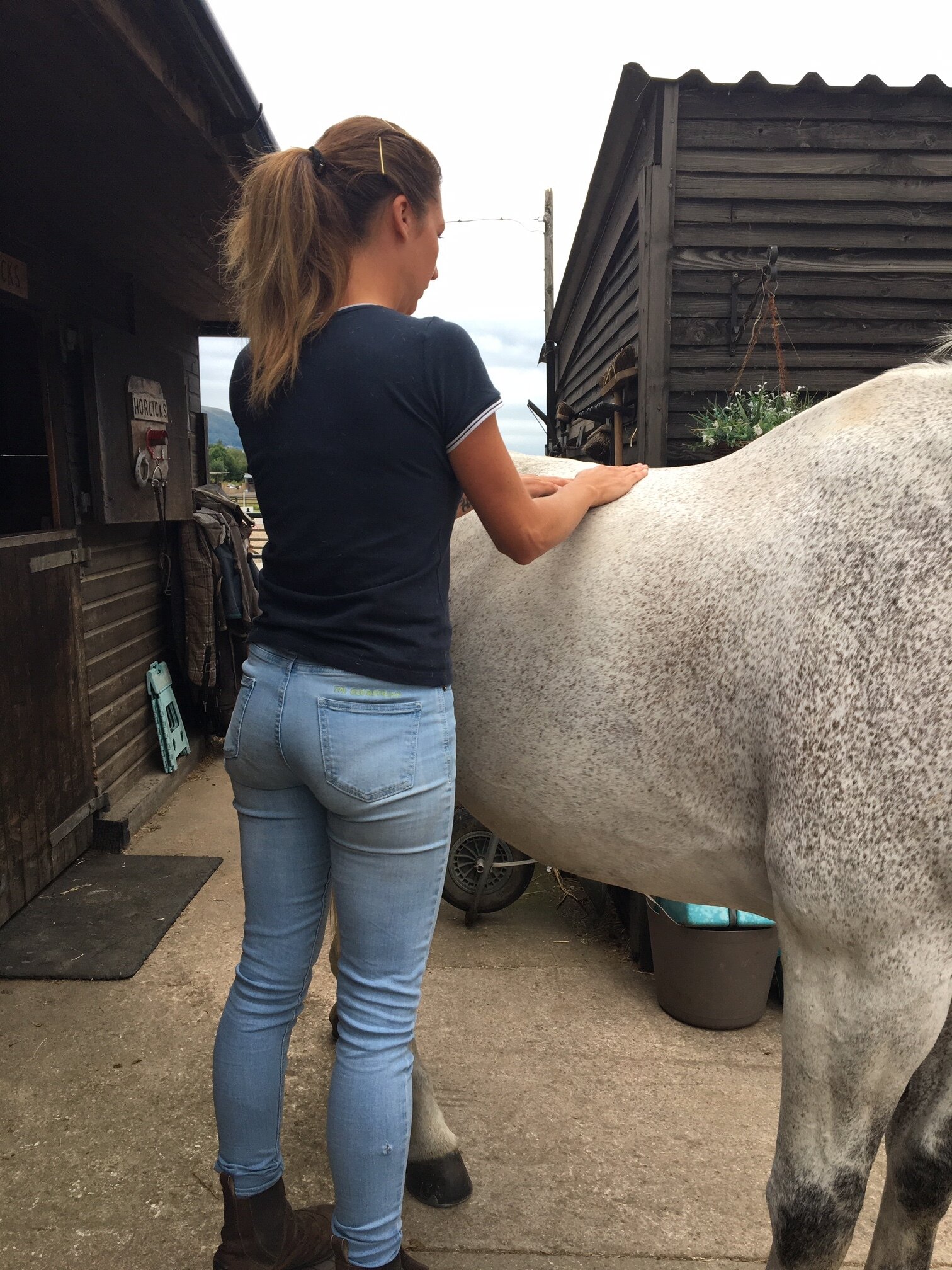
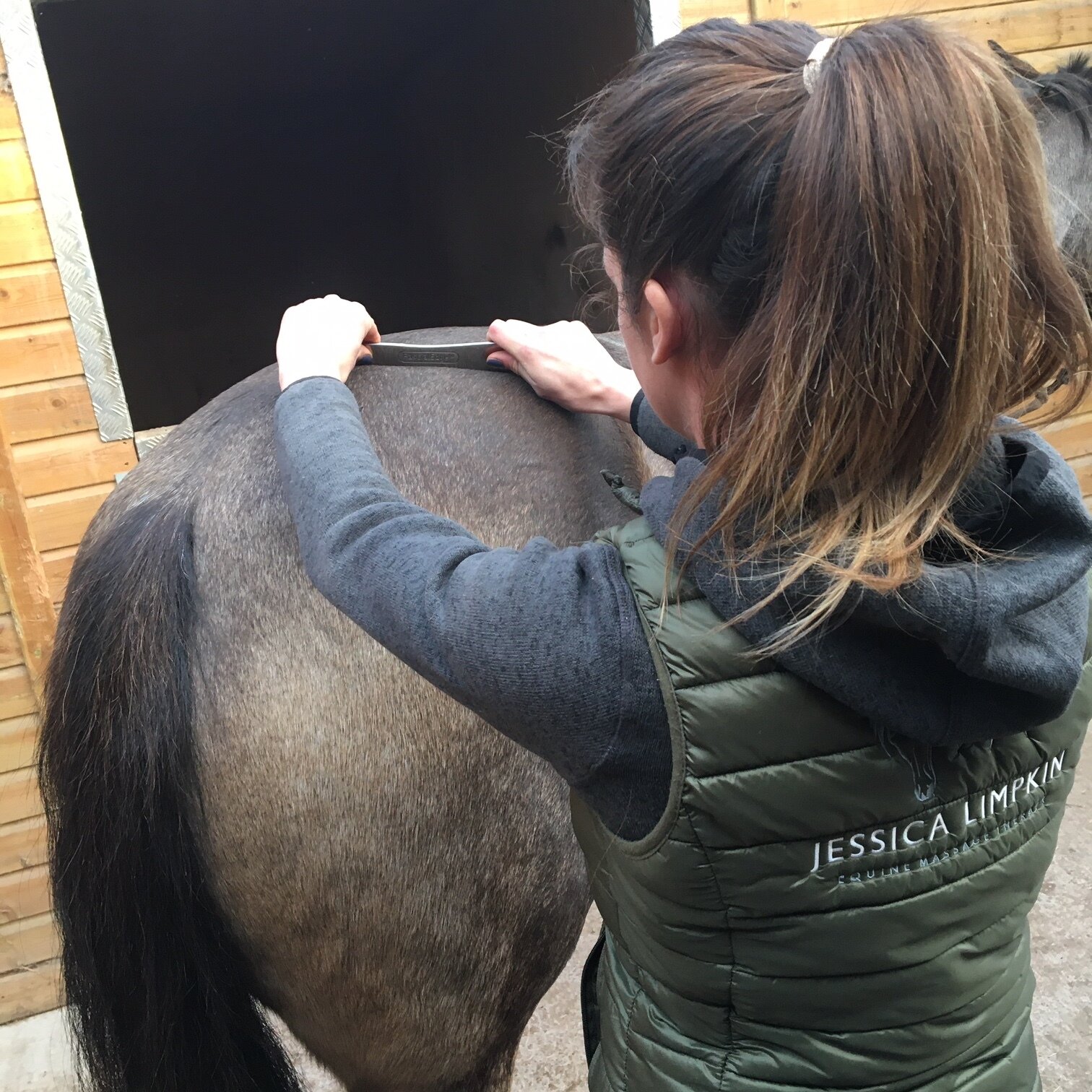
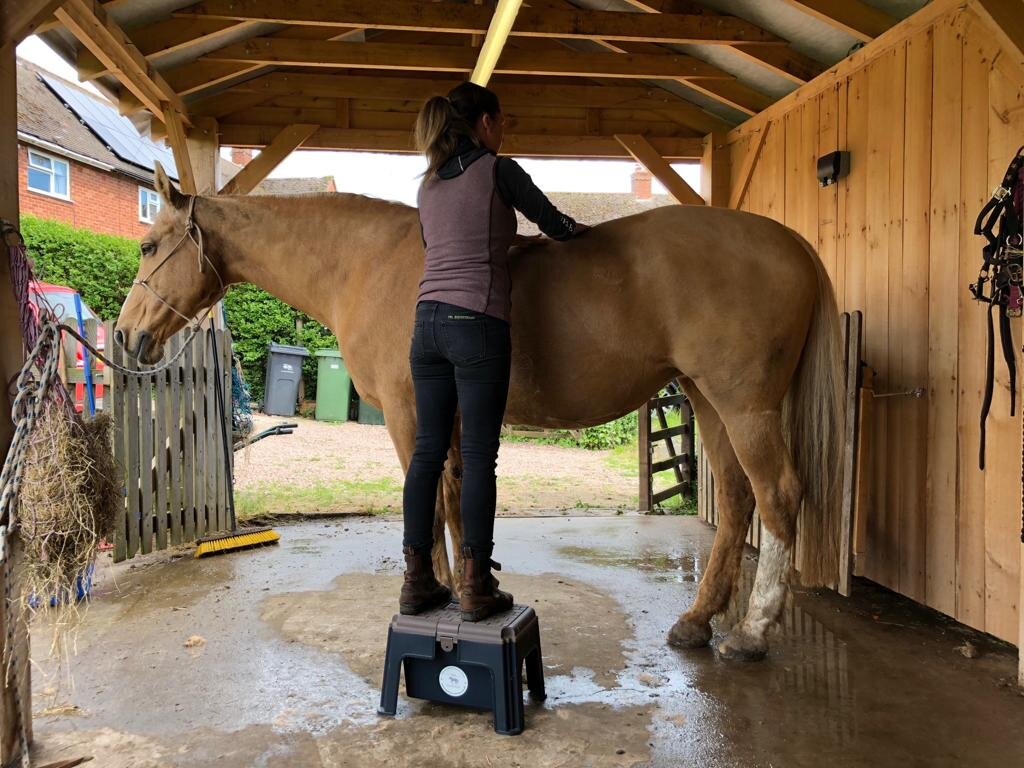
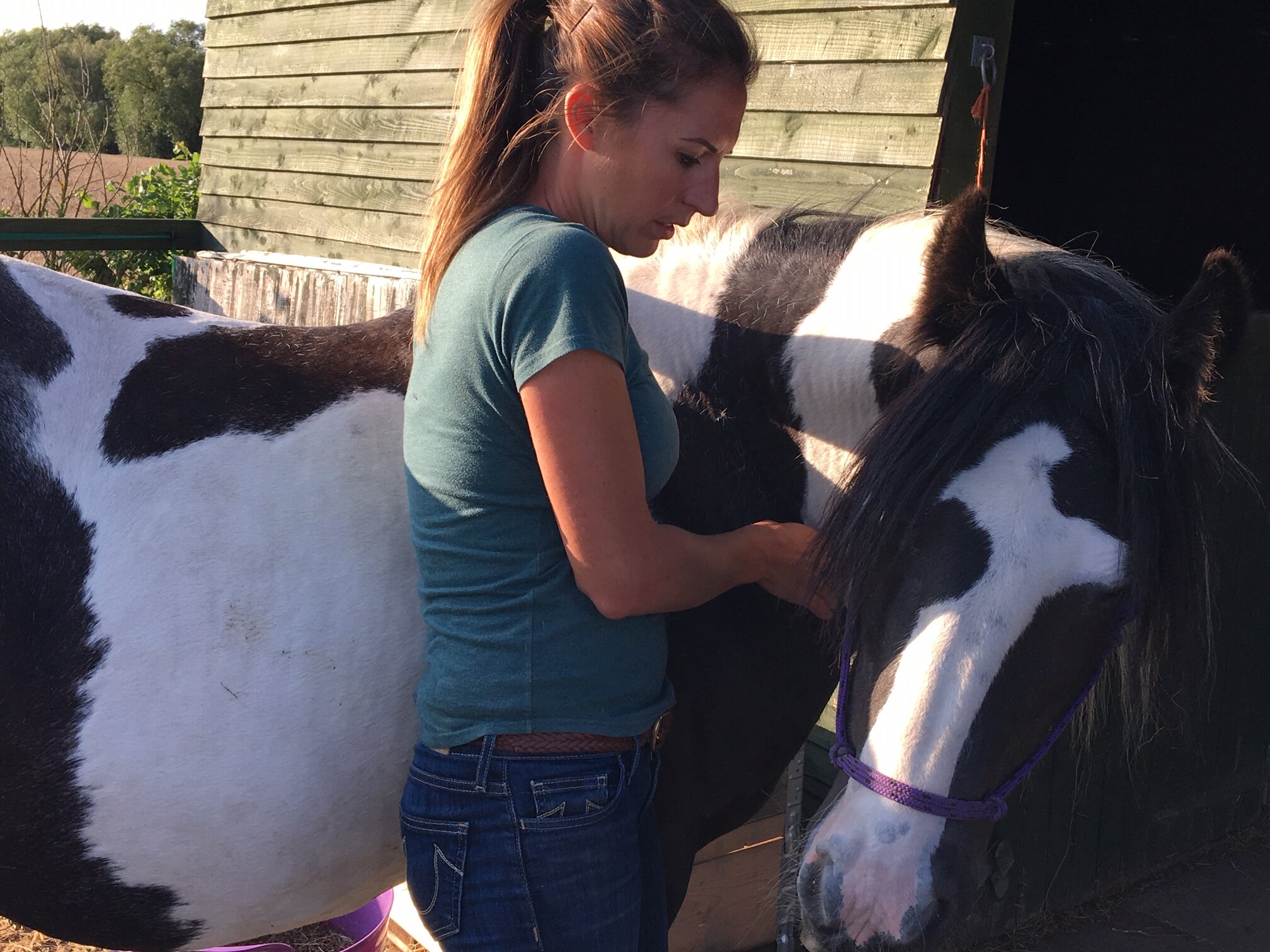
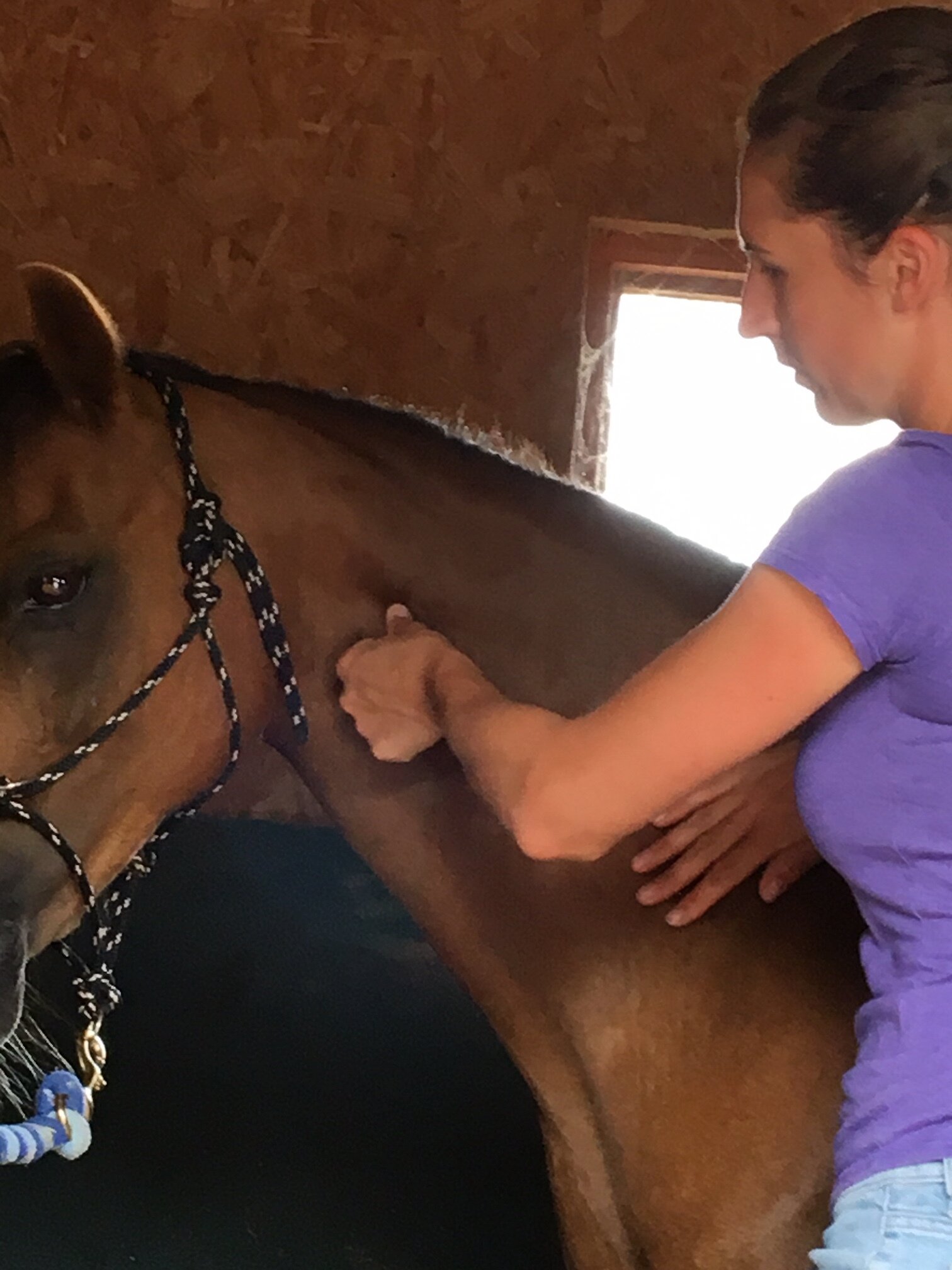
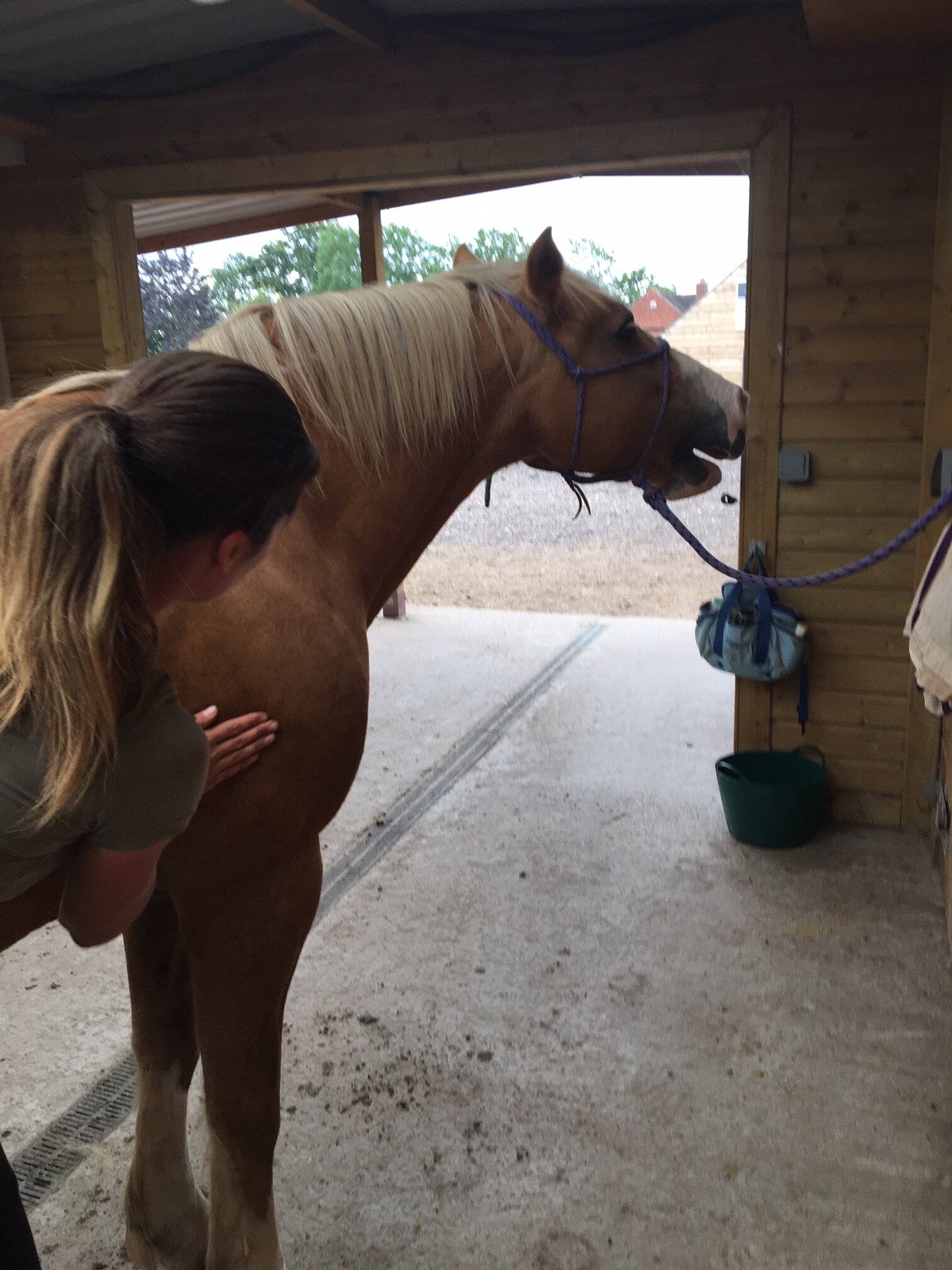
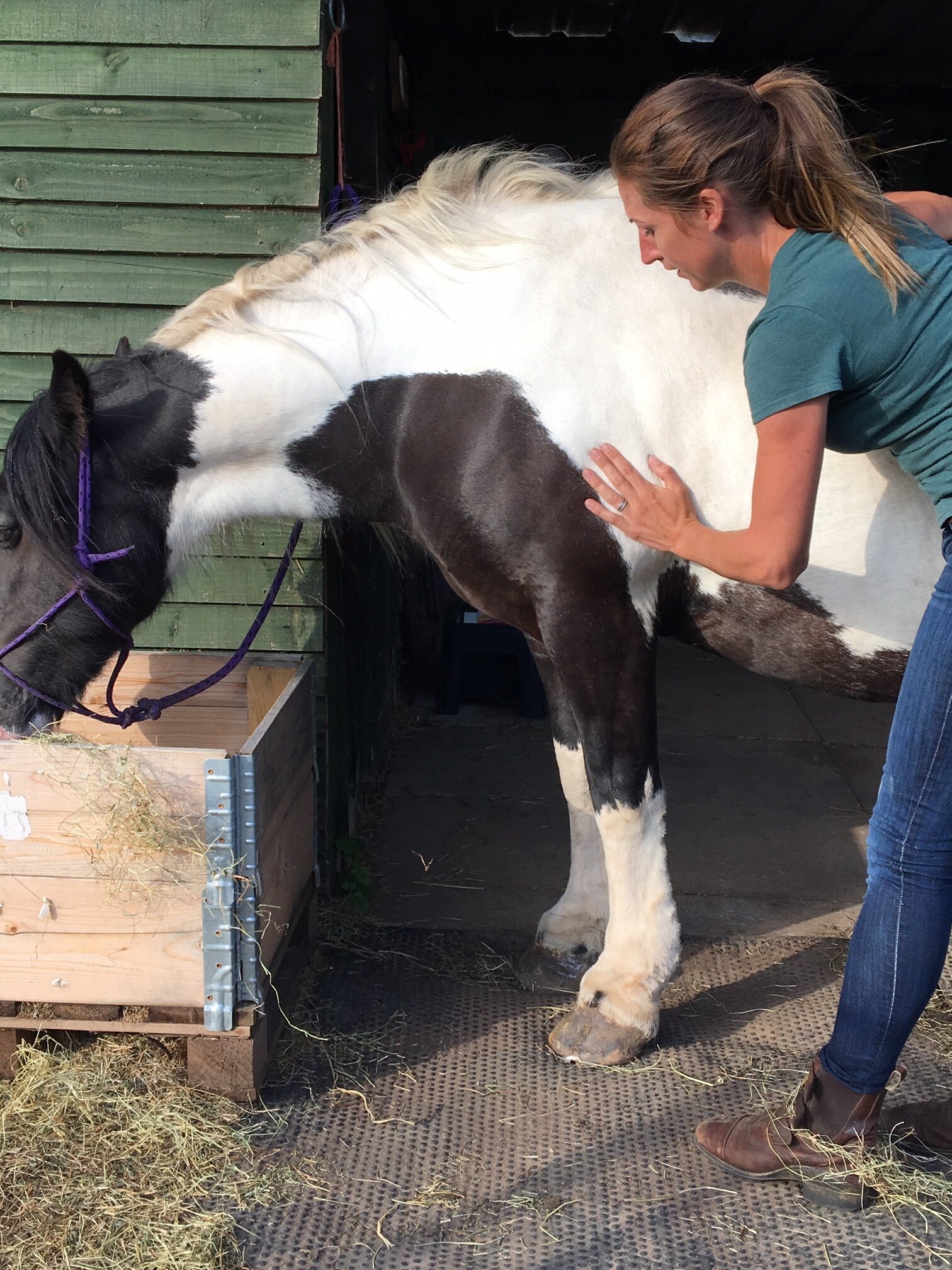
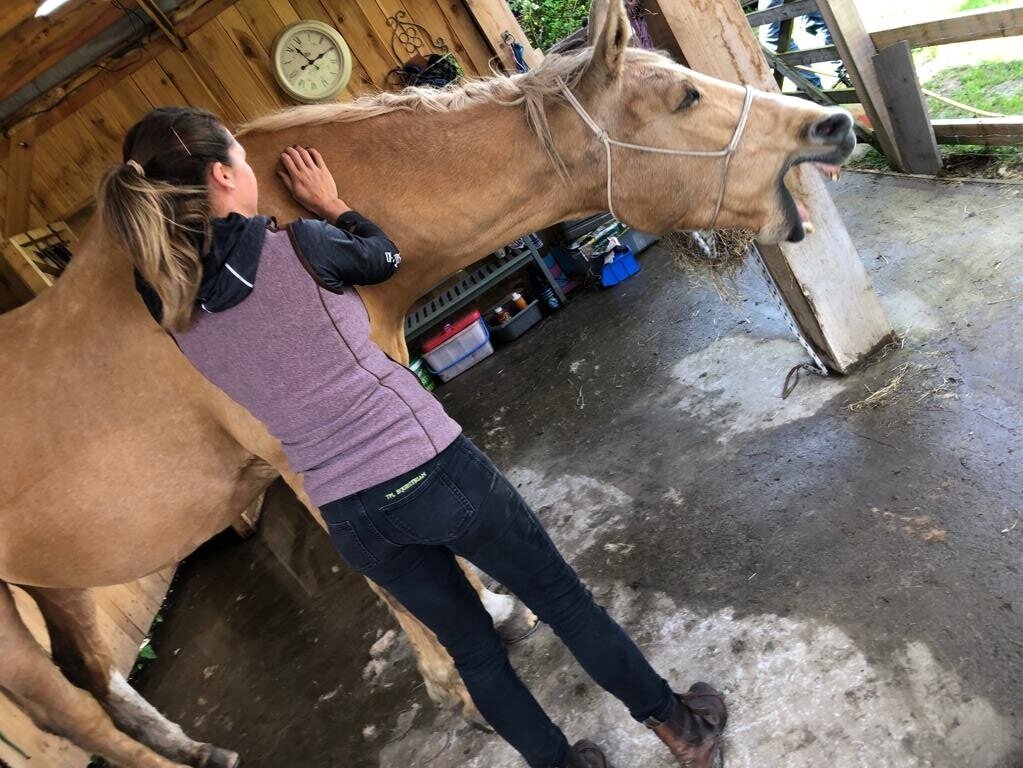
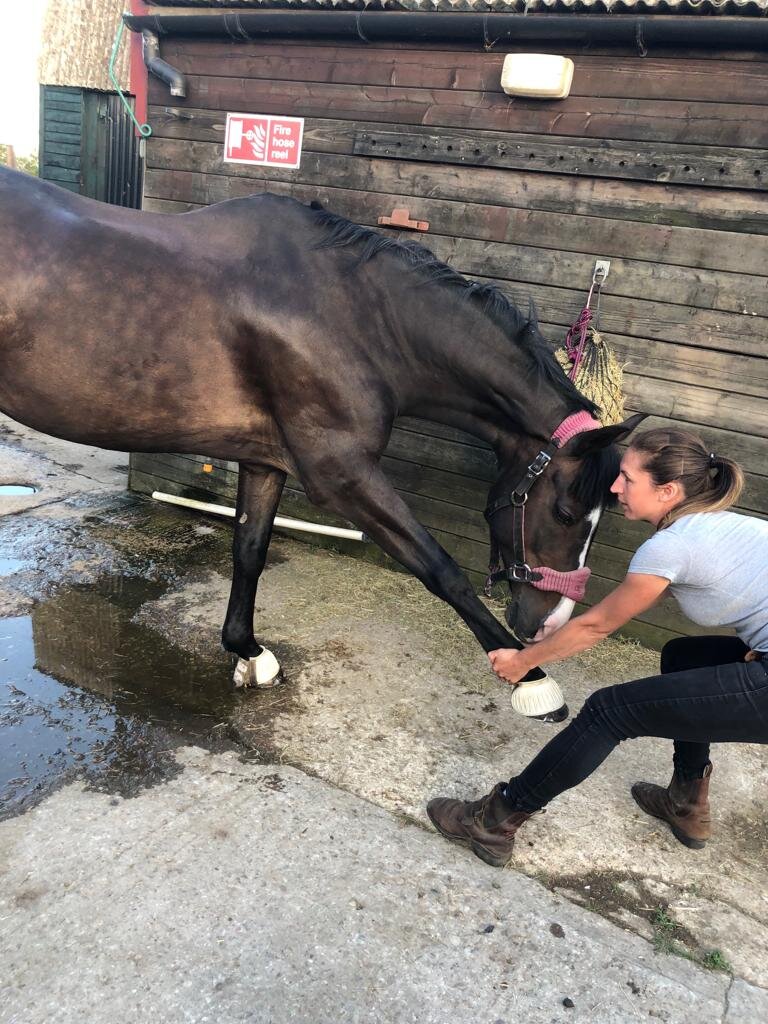
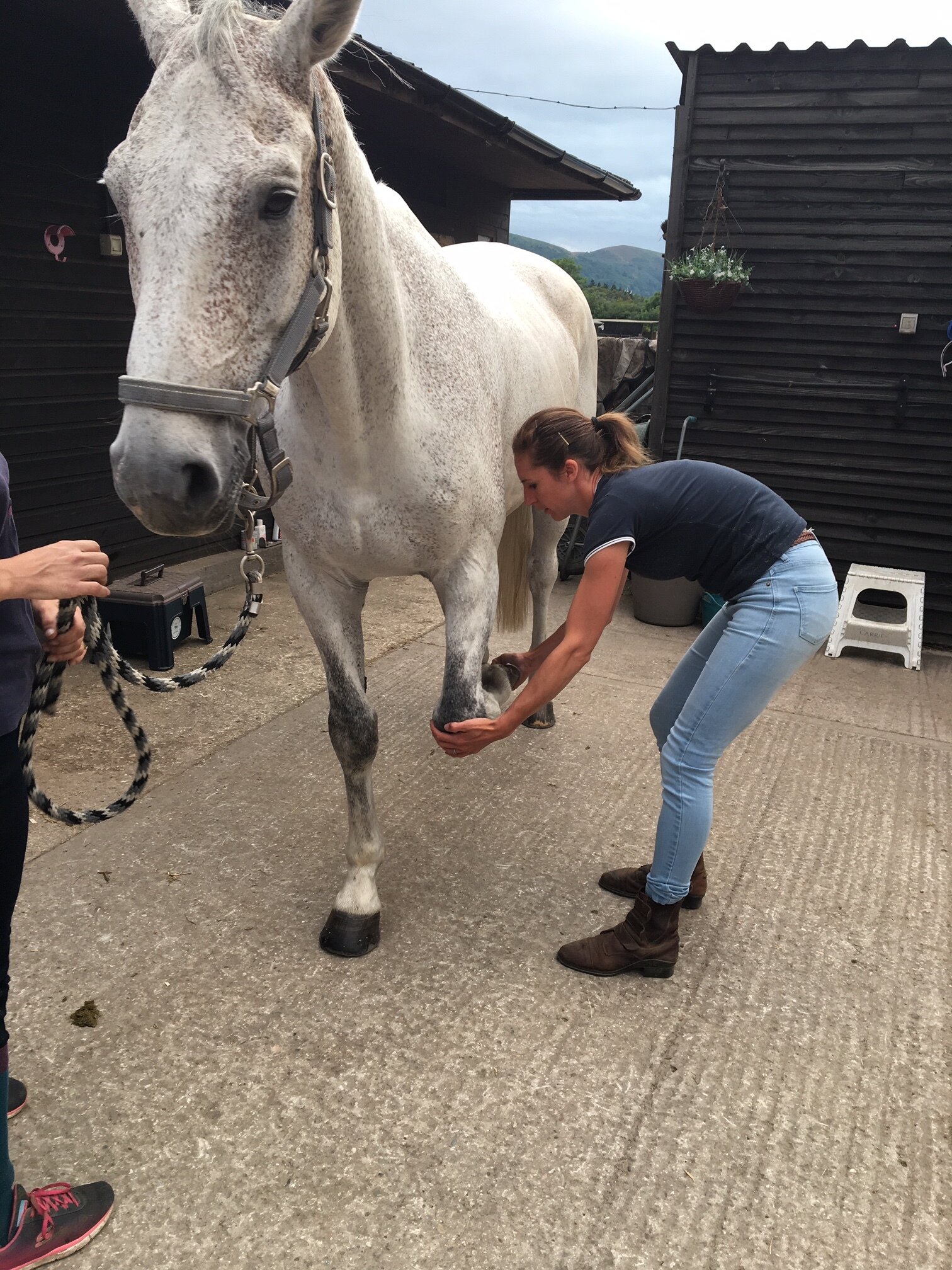
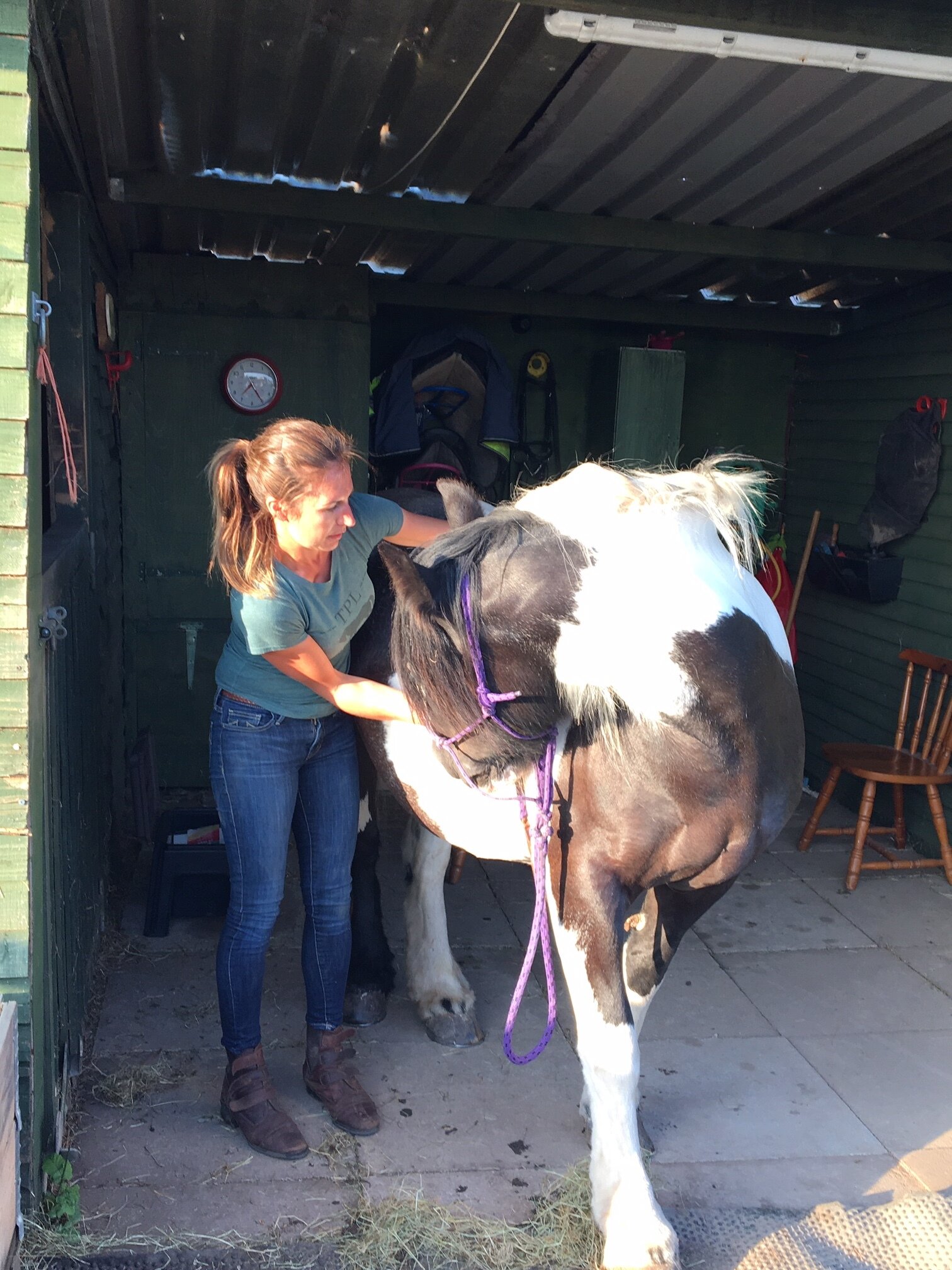
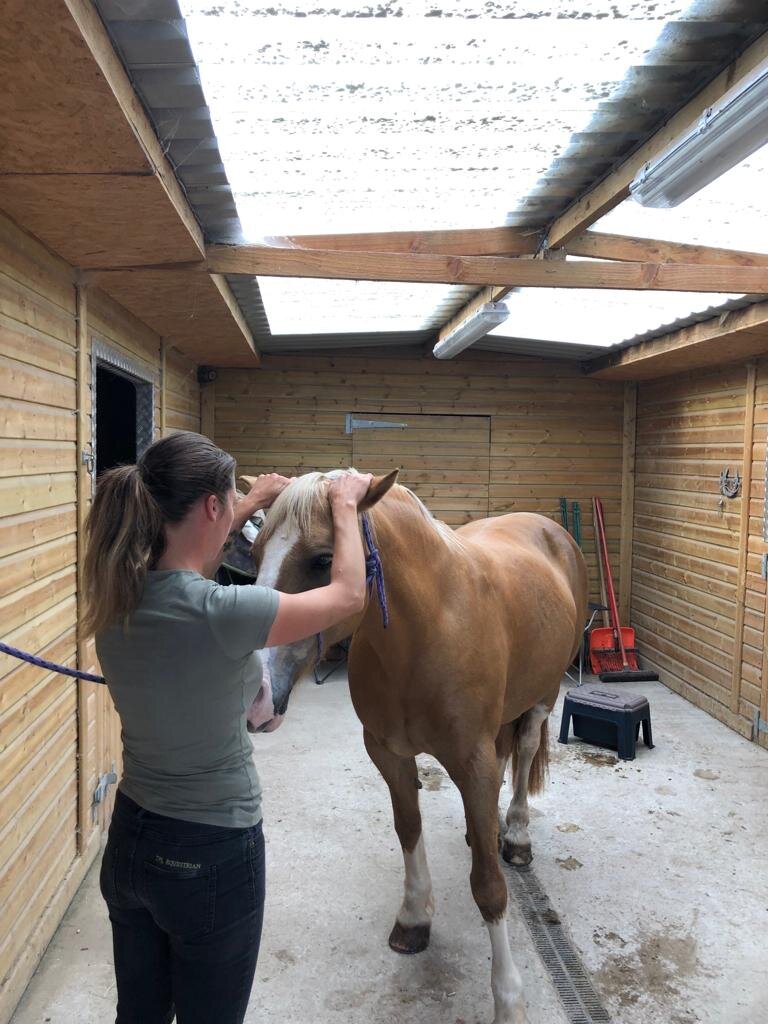
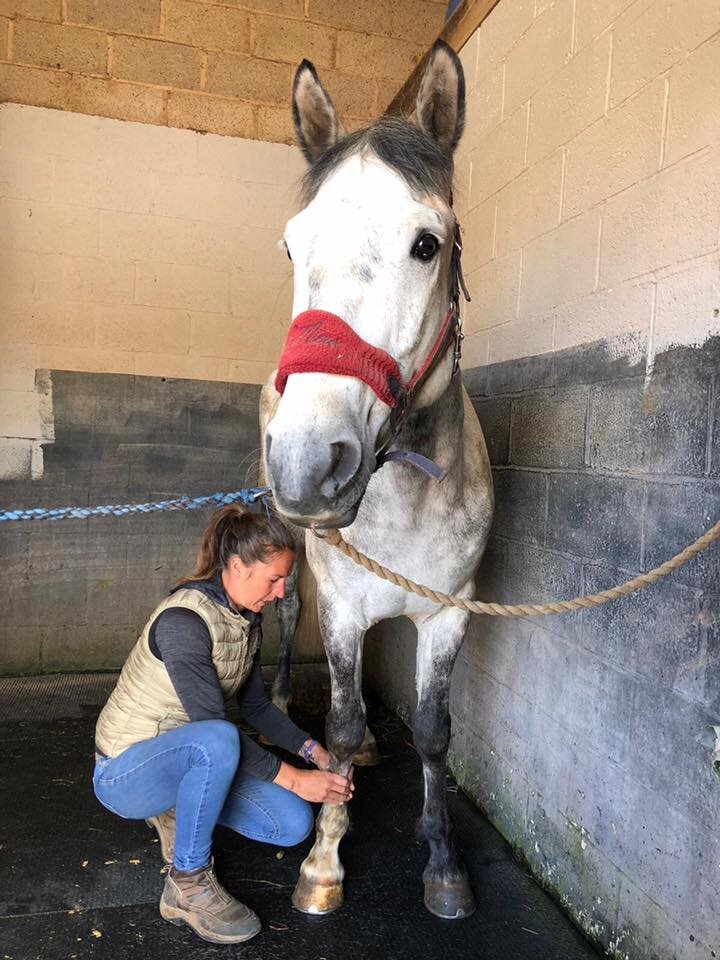
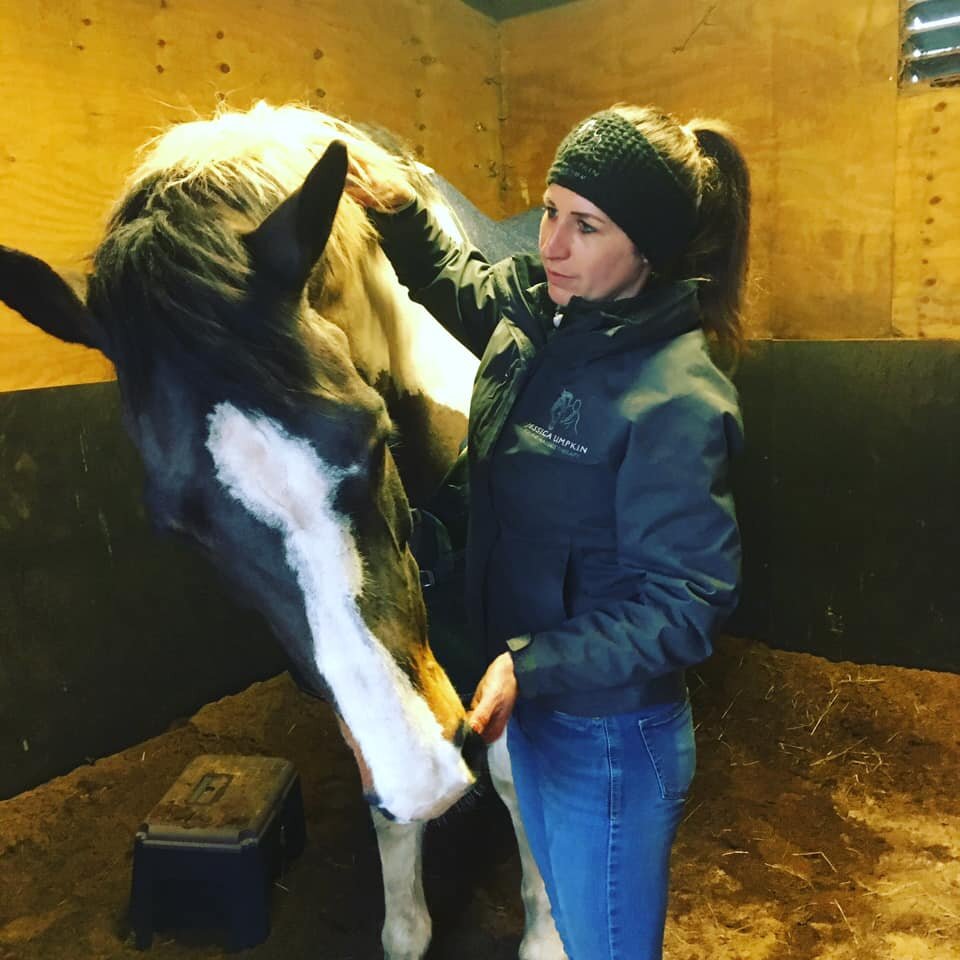
Jess will use gentle passive mobilistions as part of her treatments and will often provide you with some mobilisations specific to your horse that you can help your horse with between treatments.
Application
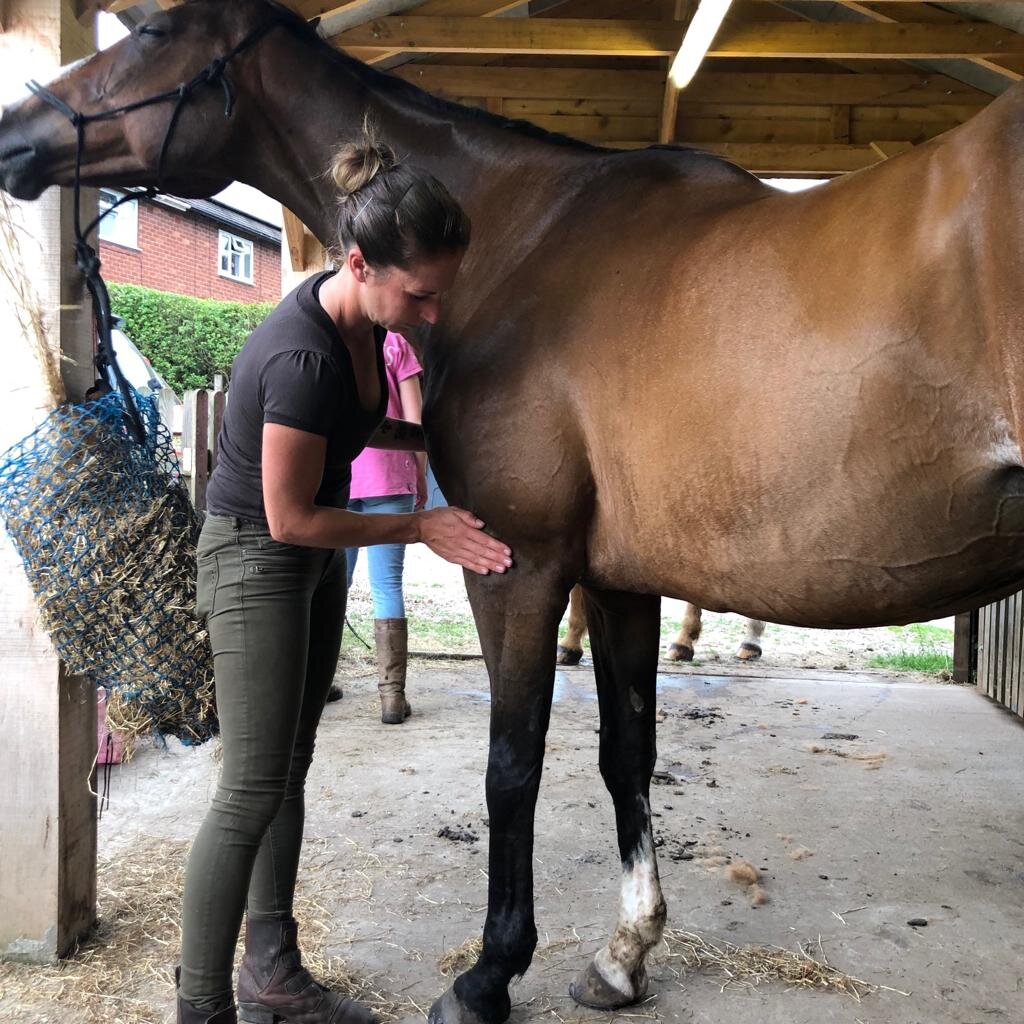
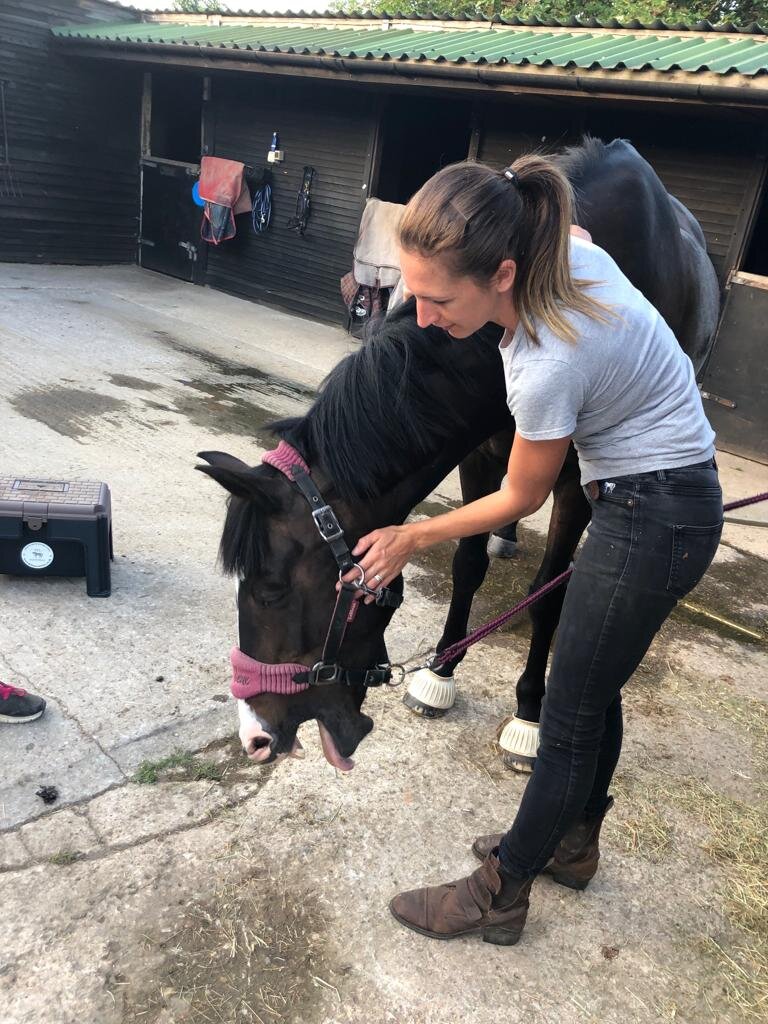
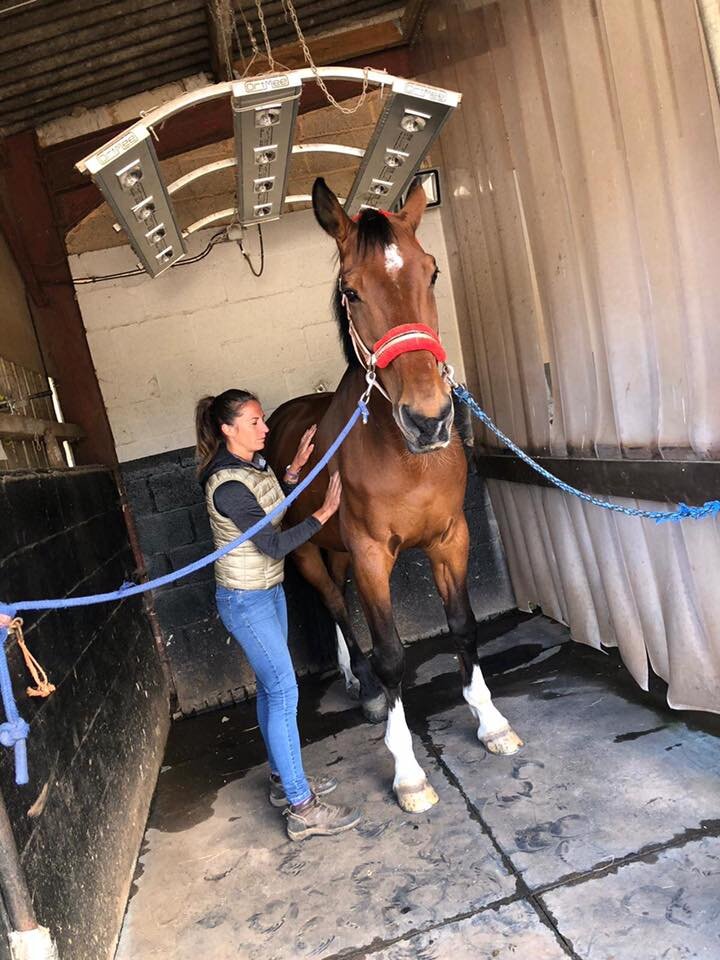
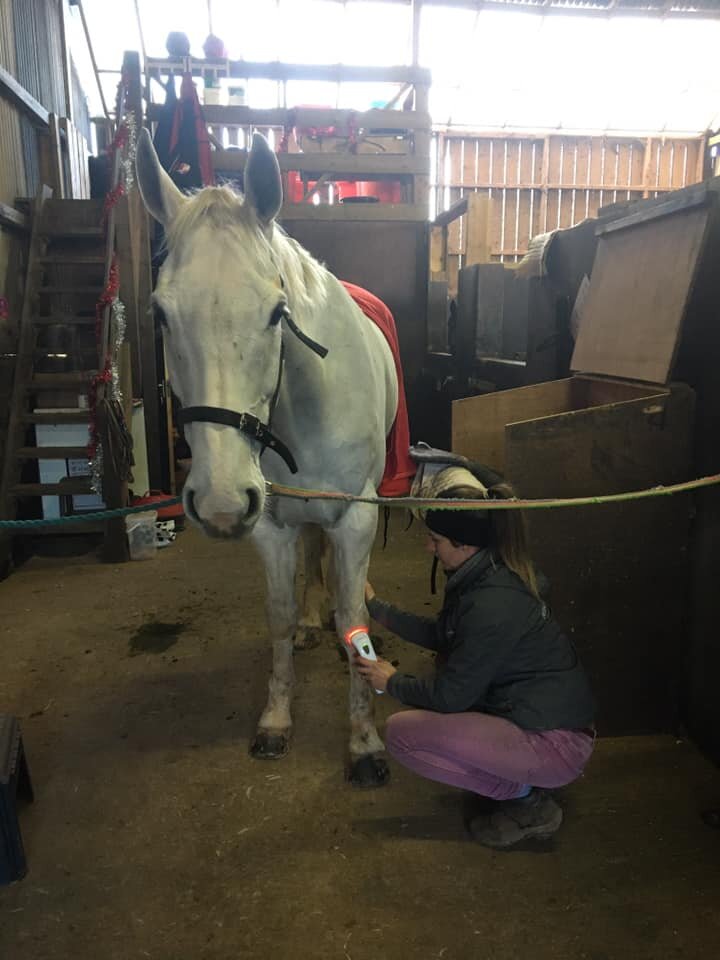
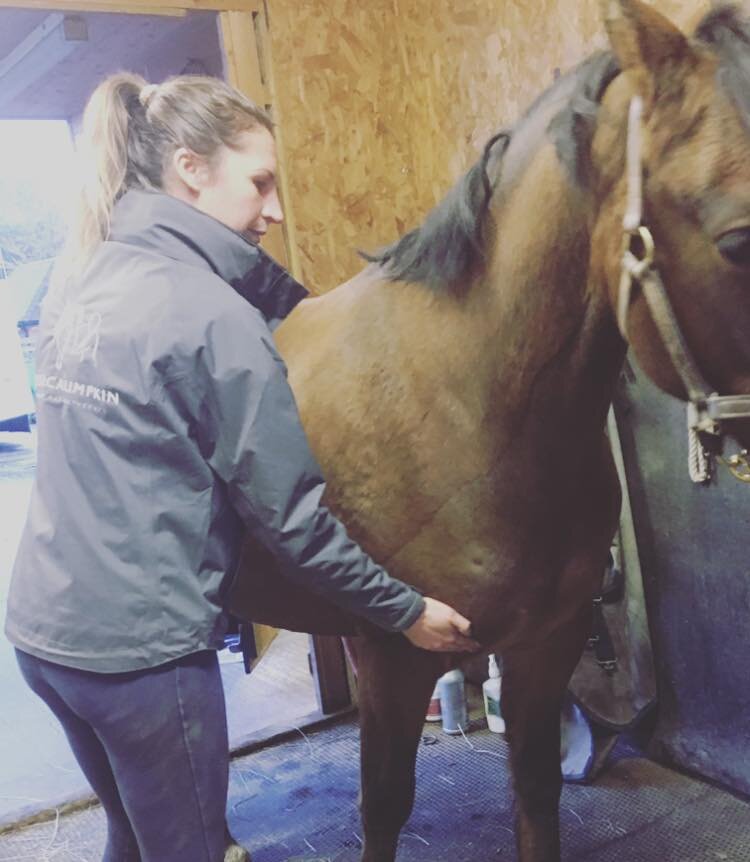
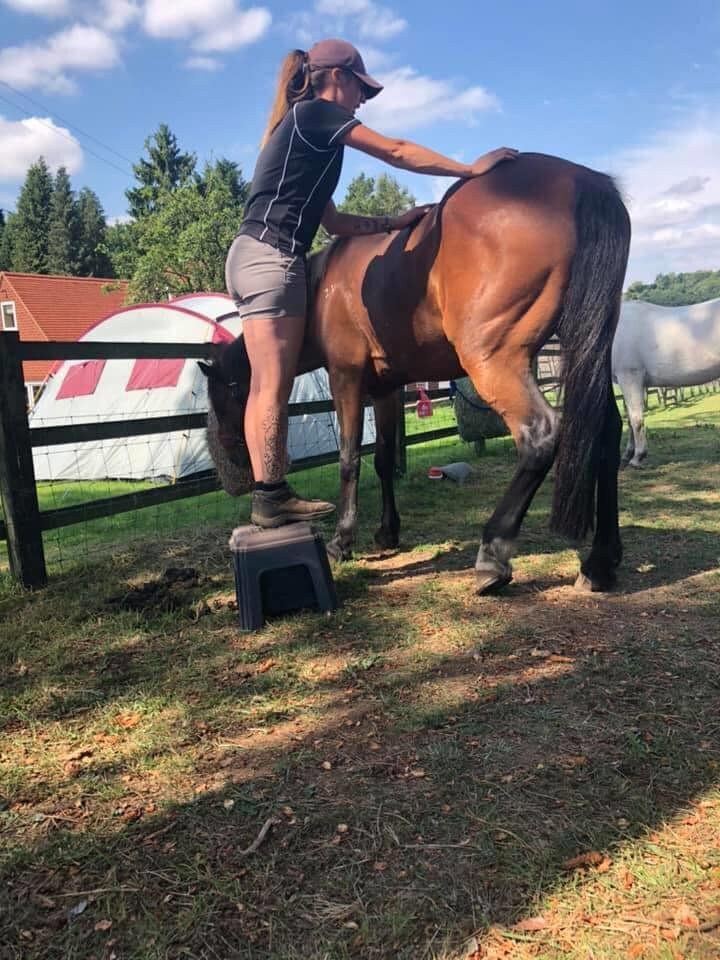
Mobilisations will be applied during treatment to help Jess assess your horse’s mobility and aid in detection of tight or immobile areas that require treatment.
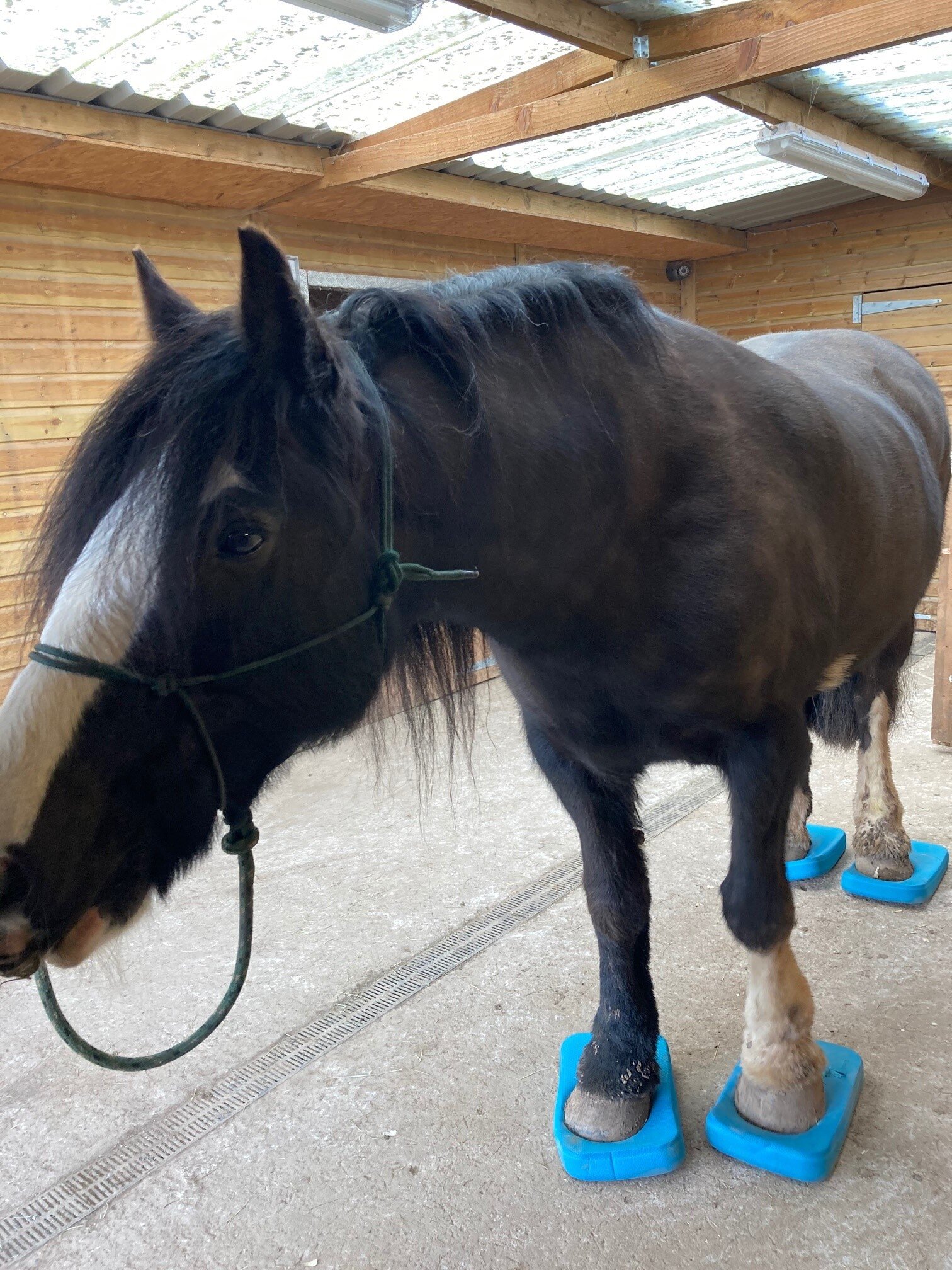
The mobilisations will be tailored to the horse’s particular muscular structure, flexibility, and varying tension levels. Being careful not to never push your horse beyond their anatomical limit.
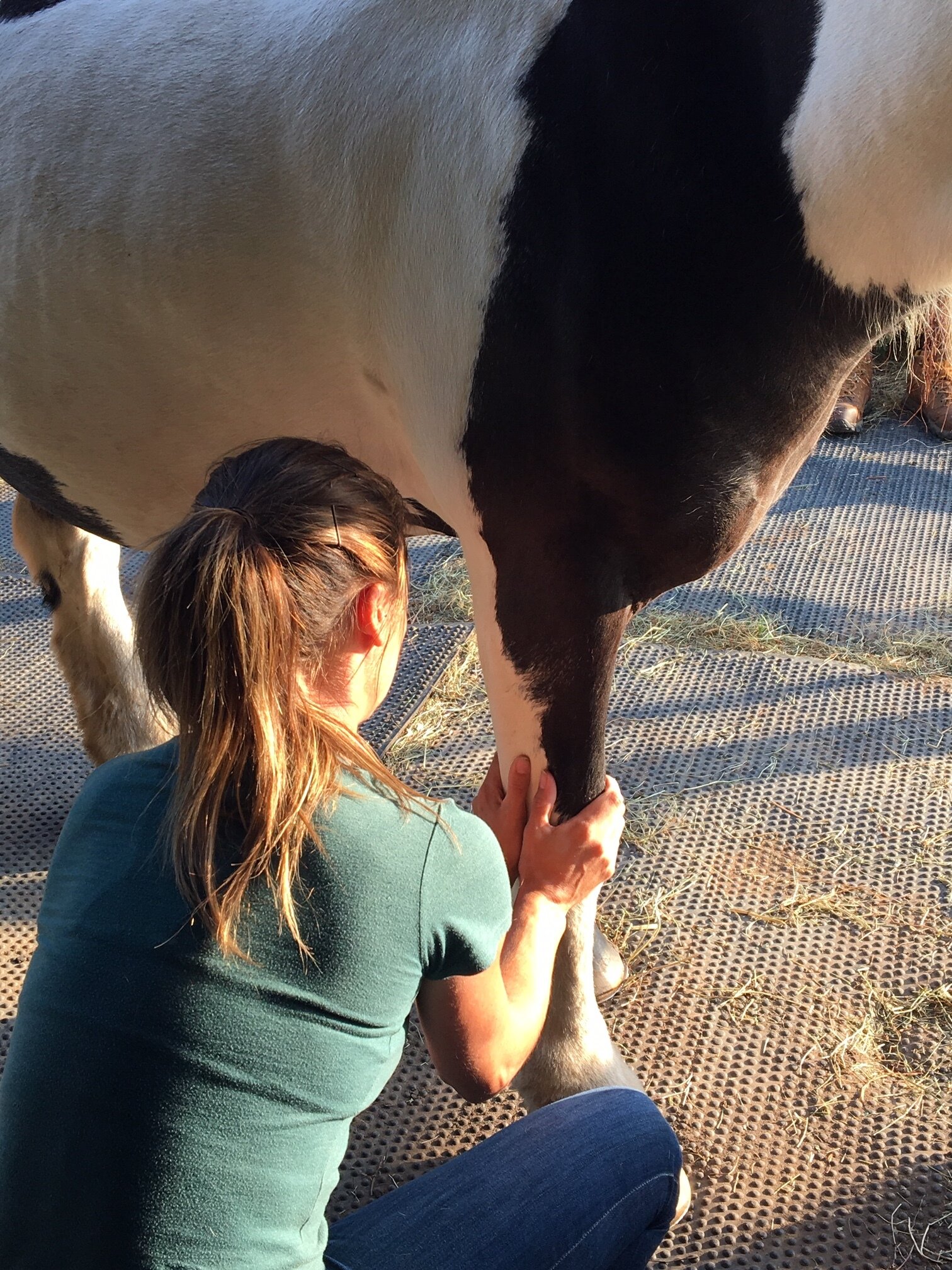
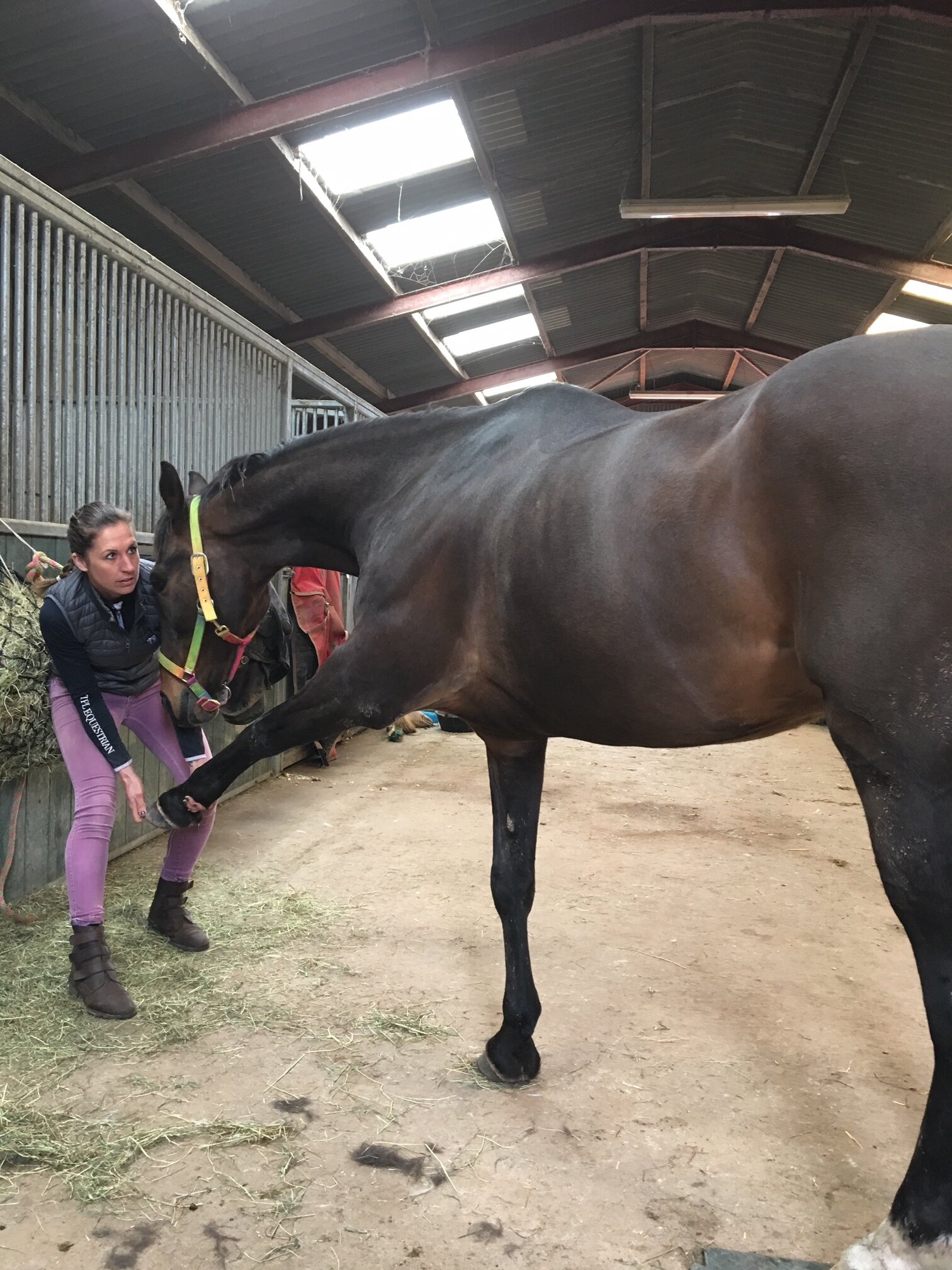
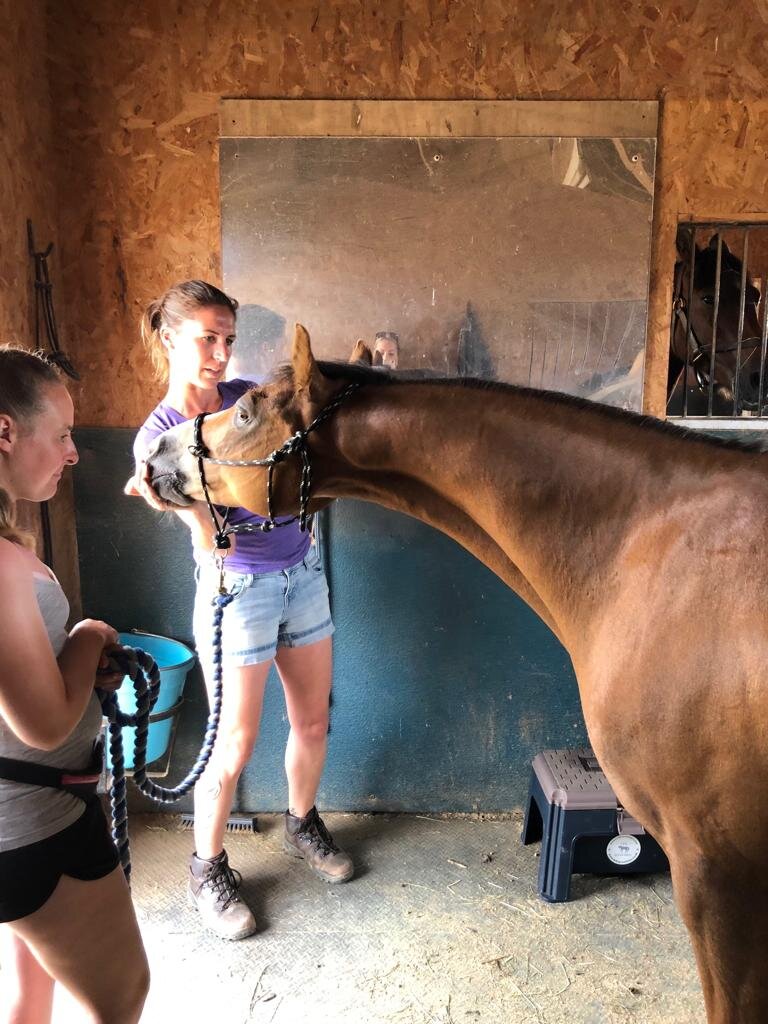
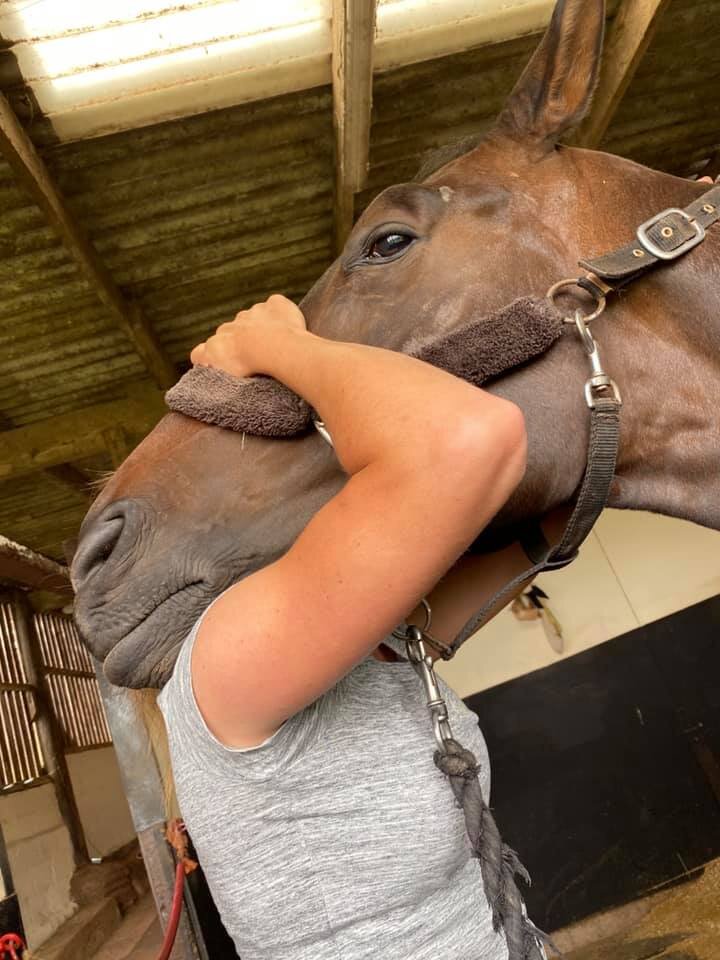
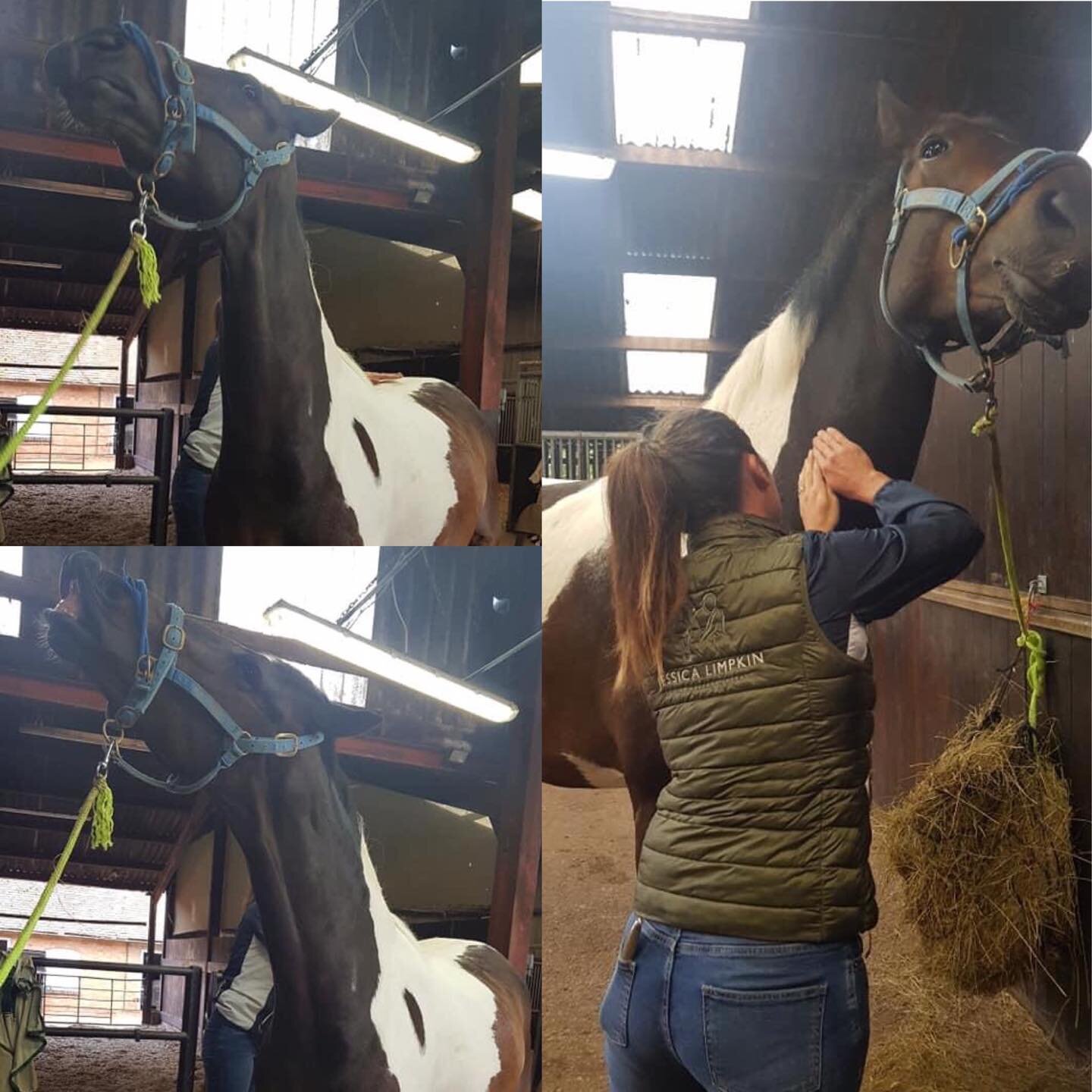
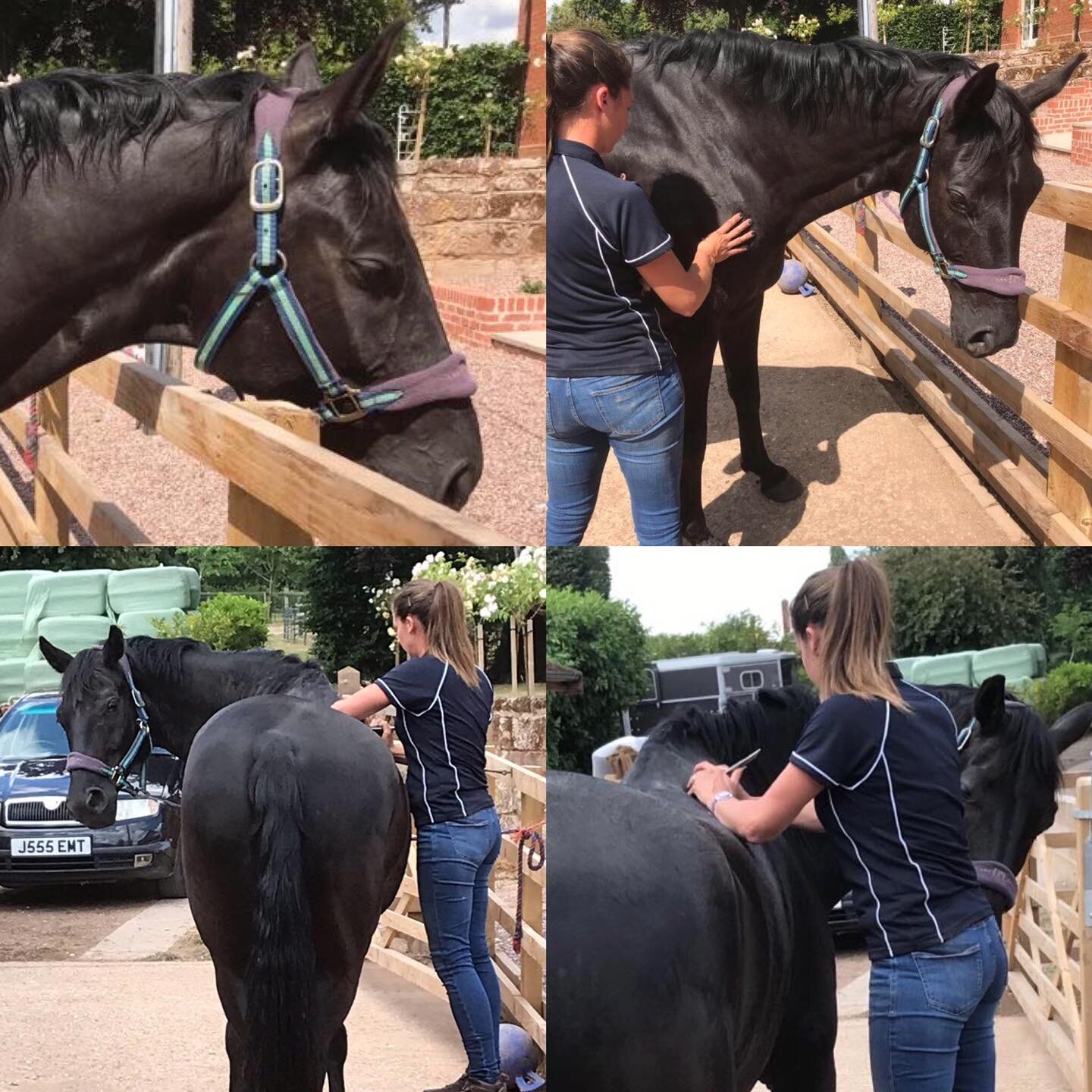
Jess will need to handle various parts of your horse’s body and will ask if your horse is used to having their feet handled before applying mobilisations involving handling the limbs.
Some of the most commonly used mobilisations are:
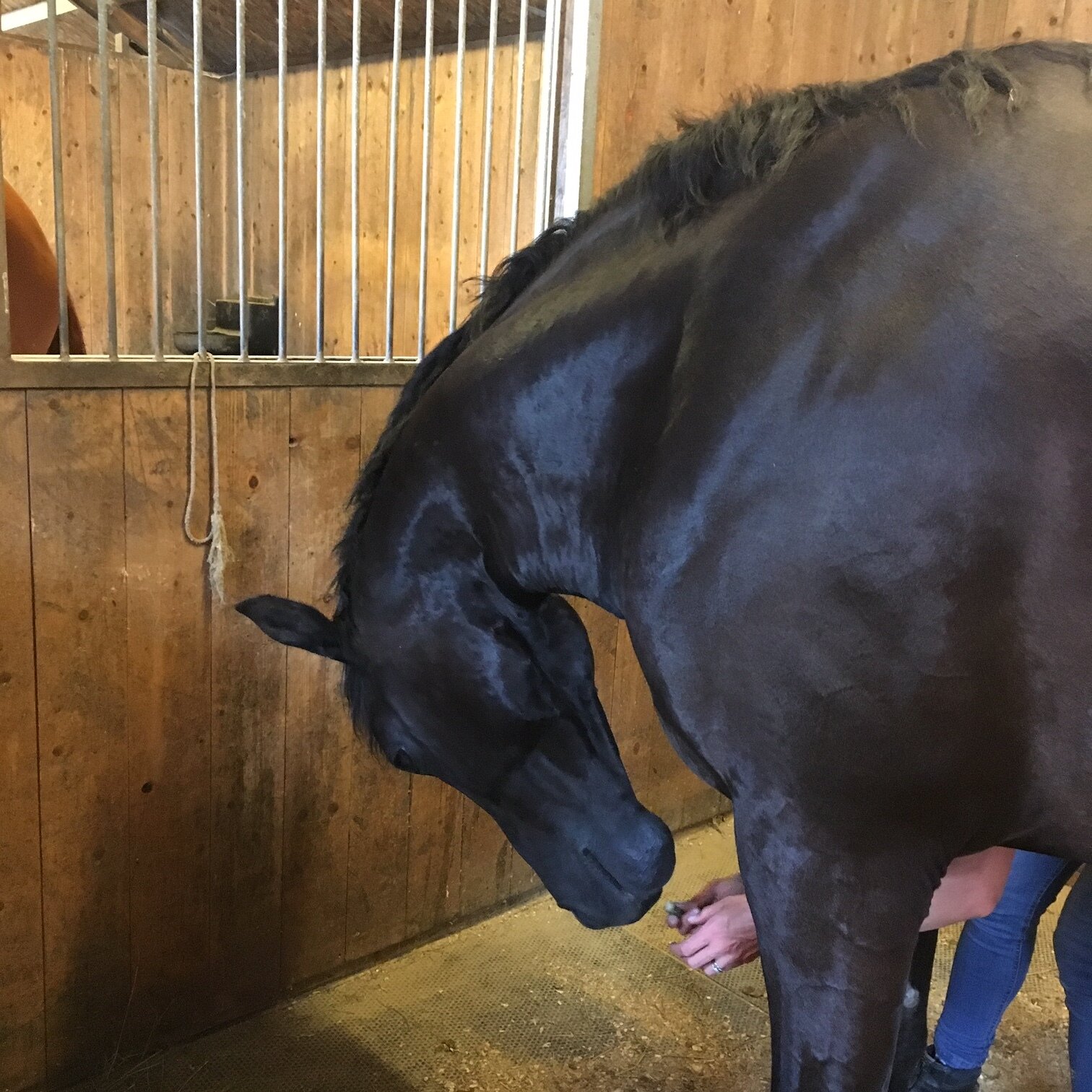
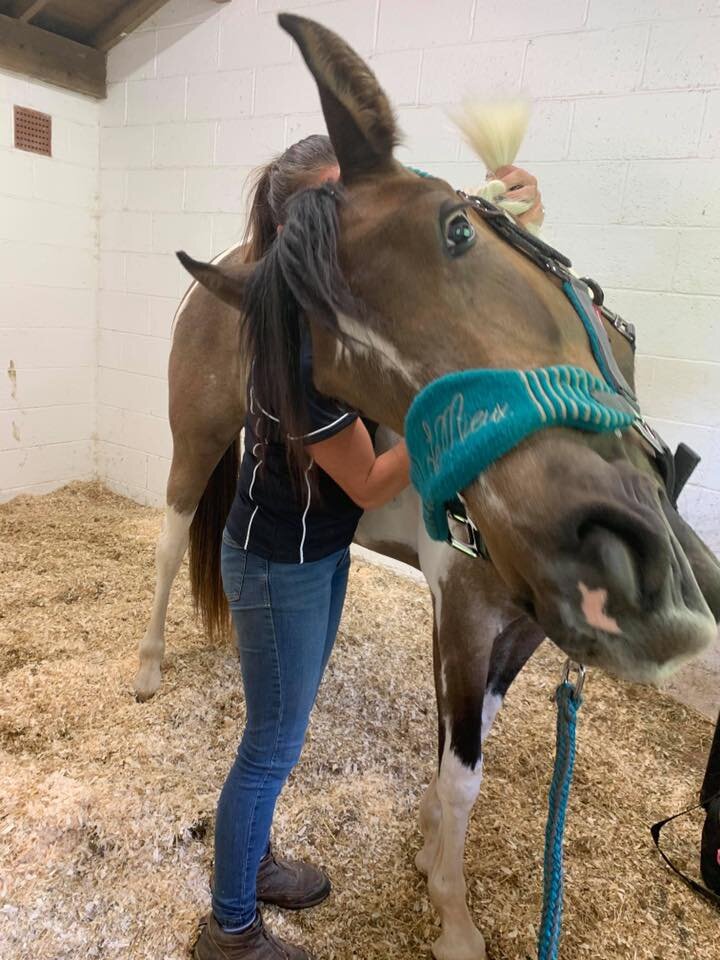
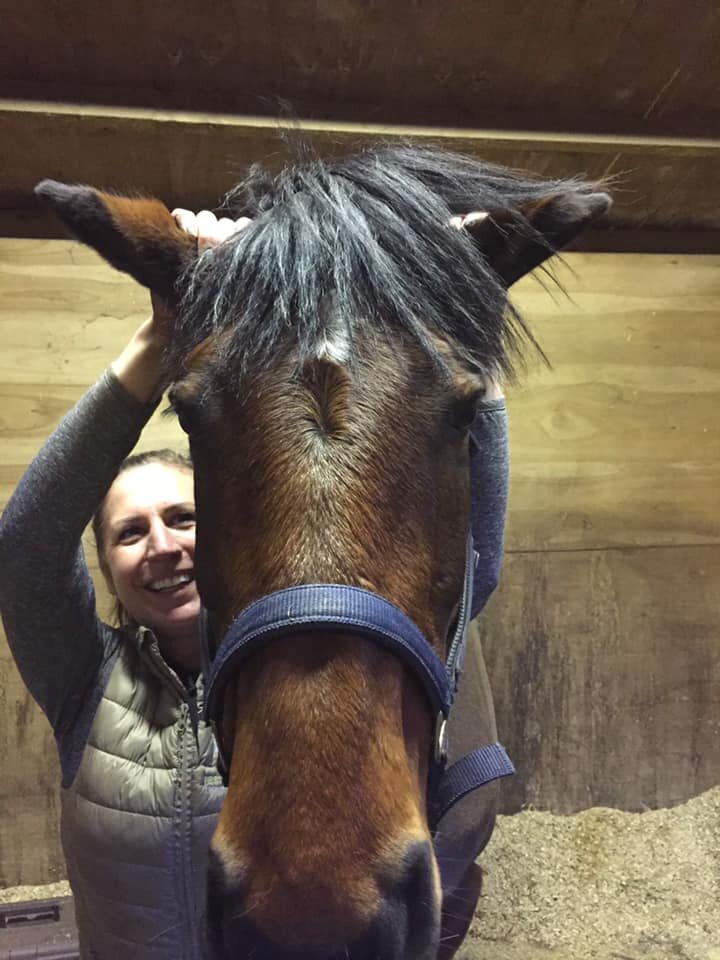
Jaw
Poll
Ears
Neck
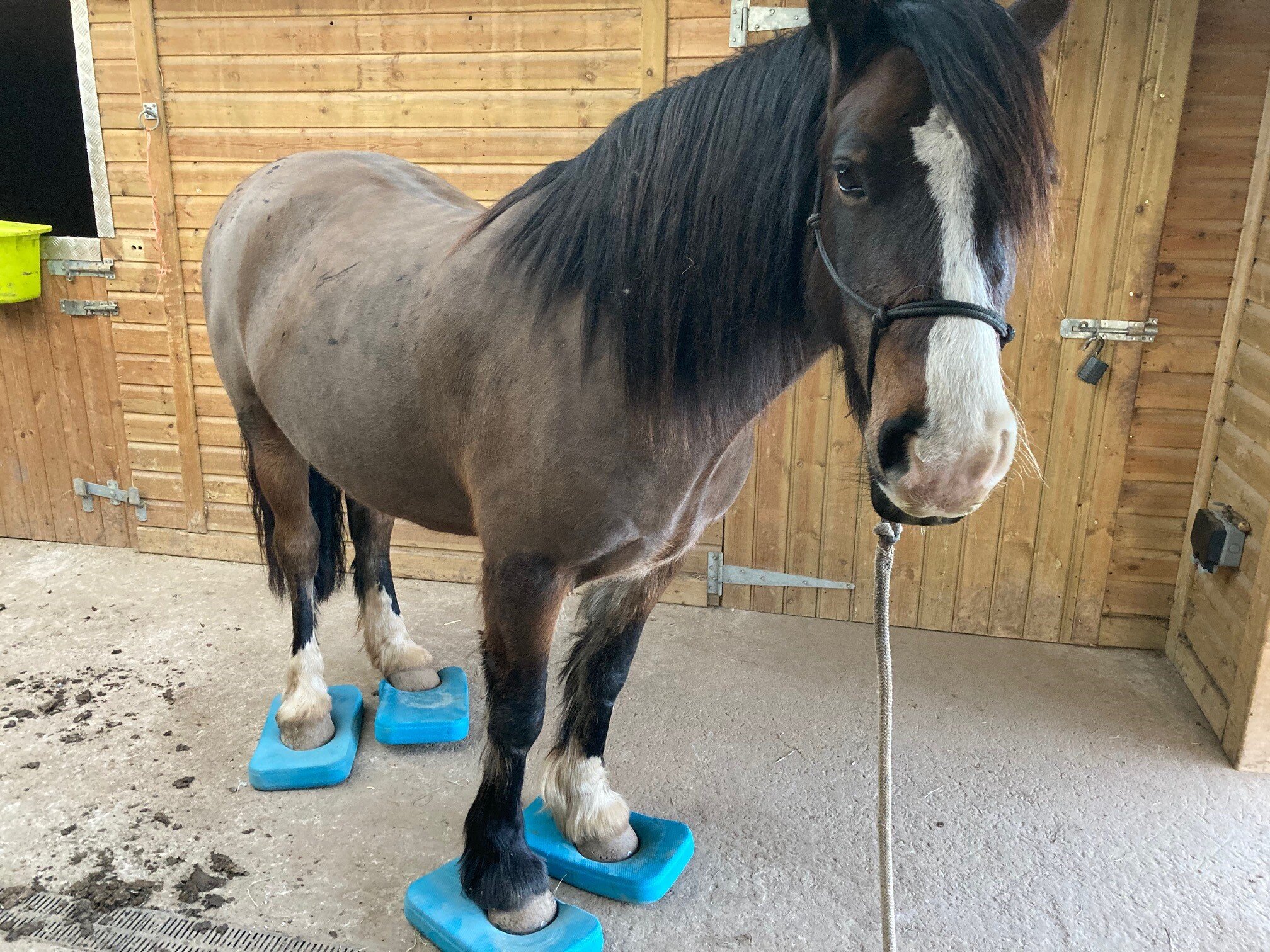
Fetlock
Knee
Elbow
Shoulder
Sternum
Withers
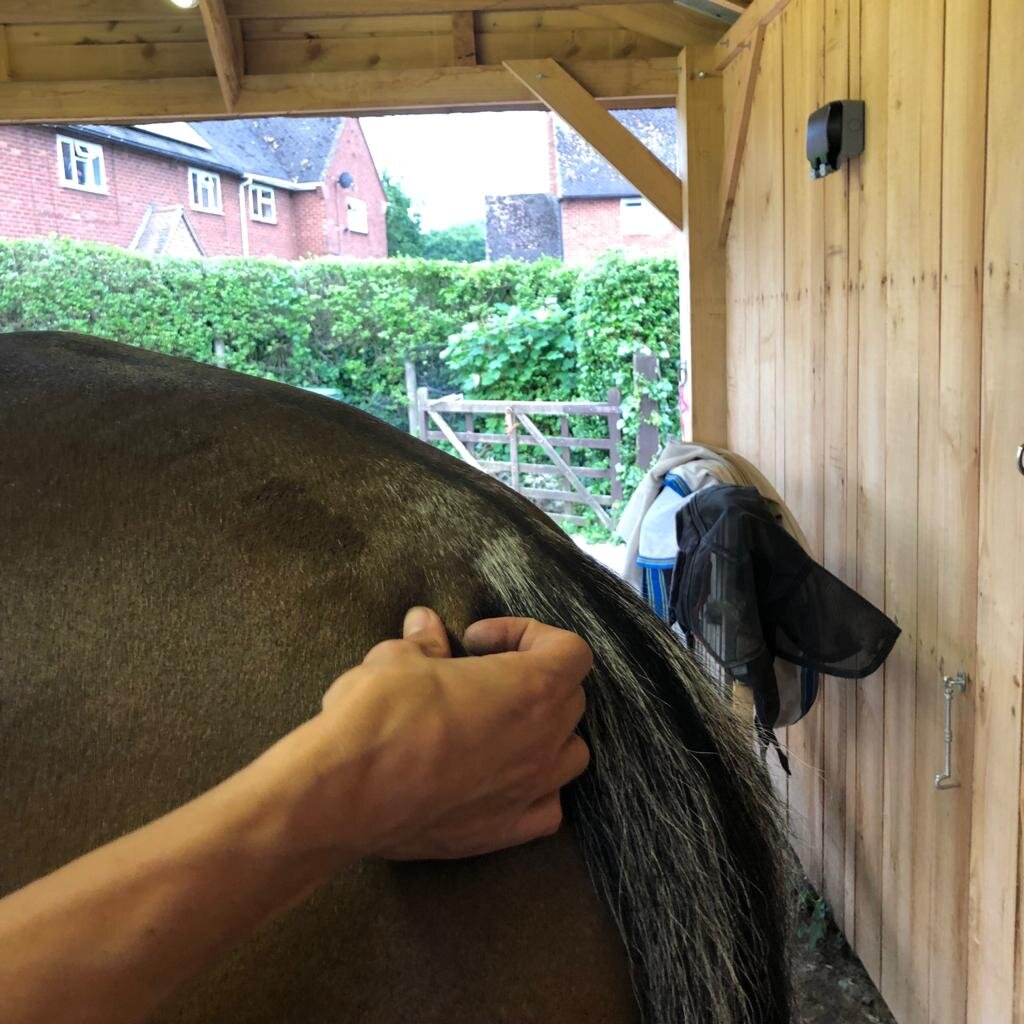
Spine
Ribs
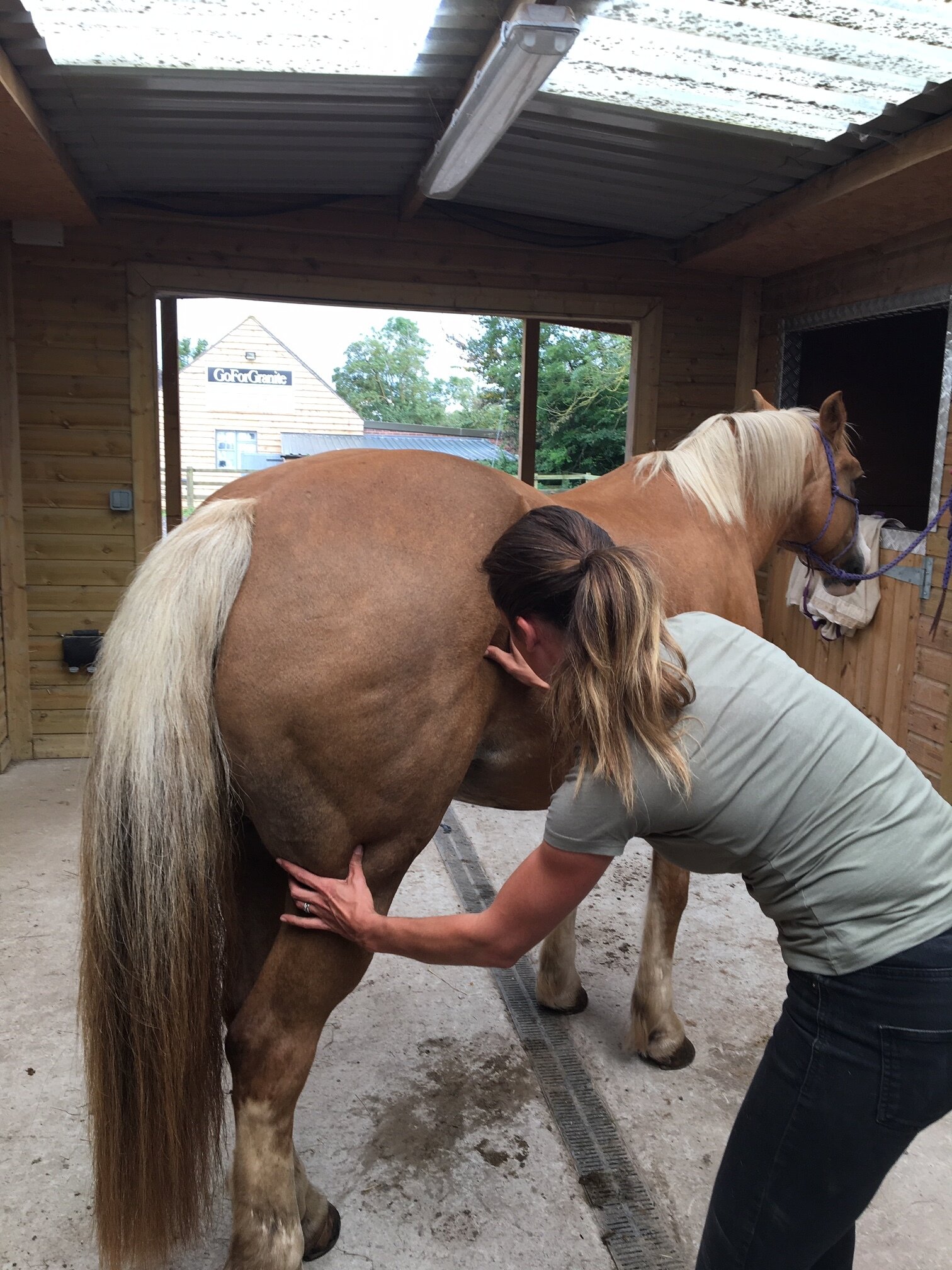
Pelvis
Hock & Stifle
Hip
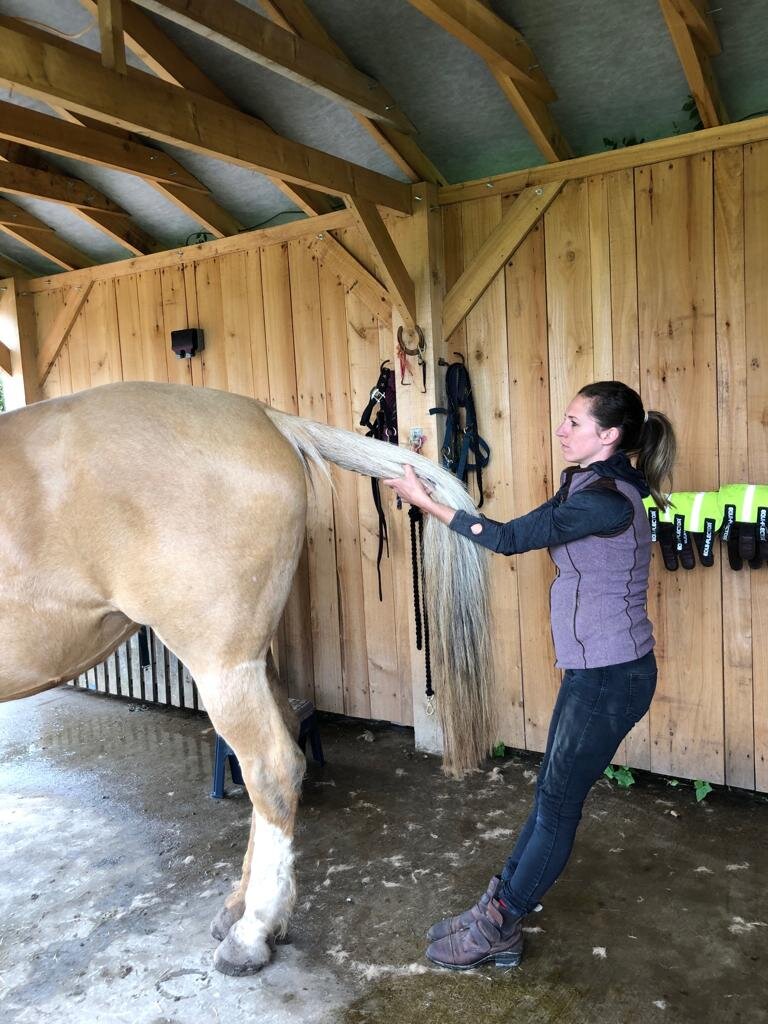
Tail
Benefits
Improves flexibility
Improves symmetry of musculoskeletal kinematics in horse
Helps restore joint mobility
Assists in reducing joint pain
Stimulates production of synovial fluid in the joints
Injury prevention
Can help correct abnormal movement patterns
Stimulates the muscles, tendons and fascia surrounding the joint